TLR7-Mediated Lupus Nephritis Is Independent of Type I IFN Signaling
- PMID: 29884703
- PMCID: PMC6039244
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701588
TLR7-Mediated Lupus Nephritis Is Independent of Type I IFN Signaling
Abstract
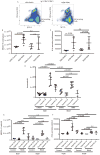
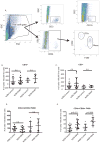
Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease characterized by increased type I IFNs, autoantibodies, and inflammatory-mediated multiorgan damage. TLR7 activation is an important contributor to systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis, but the mechanisms by which type I IFNs participate in TLR7-driven pathologic conditions remain uncertain. In this study, we examined the requirement for type I IFNs in TLR7-stimulated lupus nephritis. Lupus-prone NZM2328, INZM (which lack a functional type I IFN receptor), and NZM2328 IL-1β-/- mice were treated at 10 wk of age on the right ear with R848 (TLR7 agonist) or control (DMSO). Autoantibody production and proteinuria were assessed throughout treatment. Multiorgan inflammation was assessed at the time of decline in health. Renal infiltrates and mRNA expression were also examined after 14 d of treatment. Both NZM2328 and INZM mice exhibited a decline in survival after 3-4 wk of R848 but not vehicle treatment. Development of splenomegaly and liver inflammation were dependent on type I IFN. Interestingly, autoantibody production, early renal infiltration of dendritic cells, upregulation of IL-1β, and lupus nephritis occurred independent of type I IFN signaling. Development of TLR7-driven lupus nephritis was not abolished by the deletion of IL-1β. Thus, although IFN-α is sufficient to induce nephritis acceleration, our data emphasize a critical role for IFN-independent signaling in TLR7-mediated lupus nephritis. Further, despite upregulation of IL-1β after TLR7 stimulation, deletion of IL-1β is not sufficient to reduce lupus nephritis development in this model.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Tian J, Ma Y, Li J, Cen H, Wang DG, Feng CC, Li RJ, Leng RX, Pan HF, Ye DQ. The TLR7 7926A>G polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Molecular medicine reports. 2012;6:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Shen N, Fu Q, Deng Y, Qian X, Zhao J, Kaufman KM, Wu YL, Yu CY, Tang Y, Chen JY, Yang W, Wong M, Kawasaki A, Tsuchiya N, Sumida T, Kawaguchi Y, Howe HS, Mok MY, Bang SY, Liu FL, Chang DM, Takasaki Y, Hashimoto H, Harley JB, Guthridge JM, Grossman JM, Cantor RM, Song YW, Bae SC, Chen S, Hahn BH, Lau YL, Tsao BP. Sex-specific association of X-linked Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) with male systemic lupus erythematosus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:15838–15843. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

