Interactome analyses revealed that the U1 snRNP machinery overlaps extensively with the RNAP II machinery and contains multiple ALS/SMA-causative proteins
- PMID: 29884807
- PMCID: PMC5993797
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27136-3
Interactome analyses revealed that the U1 snRNP machinery overlaps extensively with the RNAP II machinery and contains multiple ALS/SMA-causative proteins
Abstract
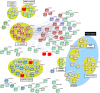
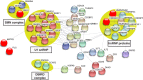
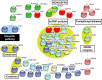
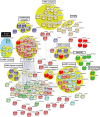
Mutations in multiple RNA/DNA binding proteins cause Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Included among these are the three members of the FET family (FUS, EWSR1 and TAF15) and the structurally similar MATR3. Here, we characterized the interactomes of these four proteins, revealing that they largely have unique interactors, but share in common an association with U1 snRNP. The latter observation led us to analyze the interactome of the U1 snRNP machinery. Surprisingly, this analysis revealed the interactome contains ~220 components, and of these, >200 are shared with the RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) machinery. Among the shared components are multiple ALS and Spinal muscular Atrophy (SMA)-causative proteins and numerous discrete complexes, including the SMN complex, transcription factor complexes, and RNA processing complexes. Together, our data indicate that the RNAP II/U1 snRNP machinery functions in a wide variety of molecular pathways, and these pathways are candidates for playing roles in ALS/SMA pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Jovicic, A., Paul, J. W., III & Gitler, A. D. Nuclear transport dysfunction: a common theme in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Journal of neurochemistry, 10.1111/jnc.13642 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

