Synergistic and low adverse effect cancer immunotherapy by immunogenic chemotherapy and locally expressed PD-L1 trap
- PMID: 29884866
- PMCID: PMC5993831
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04605-x
Synergistic and low adverse effect cancer immunotherapy by immunogenic chemotherapy and locally expressed PD-L1 trap
Abstract
Although great success has been obtained in the clinic, the current immune checkpoint inhibitors still face two challenging problems: low response rate and immune-related adverse effects (irAEs). Here we report the combination of immunogenic chemotherapy and locally expressed PD-L1 trap fusion protein for efficacious and safe cancer immunotherapy. We demonstrate that oxaliplatin (OxP) boosts anti-PD-L1 mAb therapy against murine colorectal cancer. By design of a PD-L1 trap and loading its coding plasmid DNA into a lipid-protamine-DNA nanoparticle, PD-L1 trap is produced transiently and locally in the tumor microenvironment, and synergizes with OxP for tumor inhibition. Significantly, unlike the combination of OxP and anti-PD-L1 mAb, the combination of OxP and PD-L1 trap does not induce obvious Th17 cells accumulation in the spleen, indicating better tolerance and lower tendency to irAEs. The reports here may highlight the potential of applying PD-L1 inhibitor, especially locally expressed PD-L1 trap, in cancer therapy following OxP-based chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The trap technology has been licensed to OncoTrap Inc., L.H. and R.L. are co-founders. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
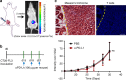
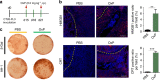




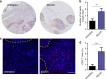
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

