Spatiotemporal dynamics in human visual cortex rapidly encode the emotional content of faces
- PMID: 29885055
- PMCID: PMC6175429
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24226
Spatiotemporal dynamics in human visual cortex rapidly encode the emotional content of faces
Abstract
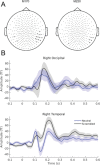
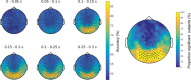
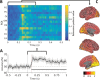
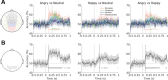
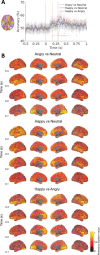
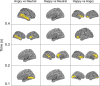
Recognizing emotion in faces is important in human interaction and survival, yet existing studies do not paint a consistent picture of the neural representation supporting this task. To address this, we collected magnetoencephalography (MEG) data while participants passively viewed happy, angry and neutral faces. Using time-resolved decoding of sensor-level data, we show that responses to angry faces can be discriminated from happy and neutral faces as early as 90 ms after stimulus onset and only 10 ms later than faces can be discriminated from scrambled stimuli, even in the absence of differences in evoked responses. Time-resolved relevance patterns in source space track expression-related information from the visual cortex (100 ms) to higher-level temporal and frontal areas (200-500 ms). Together, our results point to a system optimised for rapid processing of emotional faces and preferentially tuned to threat, consistent with the important evolutionary role that such a system must have played in the development of human social interactions.
Keywords: face perception; magnetoencephalography (MEG); multivariate pattern analysis (MVPA); threat bias.
© 2018 The Authors Human Brain Mapping Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition in the face of emotion: Characterization of the spatial-temporal dynamics that facilitate automatic emotion regulation.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Jul;39(7):2907-2916. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24048. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 29573366 Free PMC article.
-
Happy and Angry Faces Elicit Atypical Neural Activation in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2019 Dec;4(12):1021-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2019.03.013. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2019. PMID: 31171500
-
Atypical spatiotemporal activation of cerebellar lobules during emotional face processing in adolescents with autism.Hum Brain Mapp. 2021 May;42(7):2099-2114. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25349. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Hum Brain Mapp. 2021. PMID: 33528852 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: evidence from functional neuroimaging.Neuropsychologia. 2007 Jan 7;45(1):174-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.003. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Neuropsychologia. 2007. PMID: 16854439 Review.
-
Dynamics of emotional effects on spatial attention in the human visual cortex.Prog Brain Res. 2006;156:67-91. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)56004-2. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17015075 Review.
Cited by
-
Envelope Following Response to 440 Hz Carrier Chirp-Modulated Tones Show Clinically Relevant Changes in Schizophrenia.Brain Sci. 2020 Dec 27;11(1):22. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11010022. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375449 Free PMC article.
-
Neural dynamics of social verb processing: an MEG study.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2025 Jan 4;20(1):nsae066. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsae066. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39725669 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic human and avatar facial expressions elicit differential brain responses.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020 May 19;15(3):303-317. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa039. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32232359 Free PMC article.
-
It's who, not what that matters: personal relevance and early face processing.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2023 May 10;18(1):nsad021. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsad021. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37079756 Free PMC article.
-
Categorizing objects from MEG signals using EEGNet.Cogn Neurodyn. 2022 Apr;16(2):365-377. doi: 10.1007/s11571-021-09717-7. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Cogn Neurodyn. 2022. PMID: 35401863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolphs, R. (2002). Recognizing emotion from facial expressions: Psychological and neurological mechanisms. Current Opinions in Neurobiology, 1(1), 21–177. - PubMed
-
- Aguado, L. , Valdés‐Conroy, B. , Rodríguez, S. , Román, F. J. , Diéguez‐Risco, T. , & Fernández‐Cahill, M. (2012). Modulation of early perceptual processing by emotional expression and acquired valence of faces: An ERP study. Journal of Psychophysiology, 26(1), 29–41.
-
- Balconi, M. , & Pozzoli, U. (2003). Face‐selective processing and the effect of pleasant and unpleasant emotional expressions on ERP correlates. International Journal of Psychophysiology: Official Journal of the International Organization of Psychophysiology, 49(1), 67–74. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, M. , & Yovel, G. (2015). Two neural pathways of face processing: A critical evaluation of current models. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 55, 536–546. - PubMed
-
- Brainard, D. H. (1997). The psychophysics toolbox. Spatial Vision, 10(4), 433–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

