Aerobic exercise modulates anticipatory reward processing via the μ-opioid receptor system
- PMID: 29885086
- PMCID: PMC6866313
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.24224
Aerobic exercise modulates anticipatory reward processing via the μ-opioid receptor system
Abstract
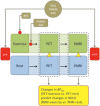
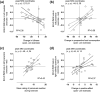
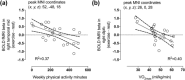
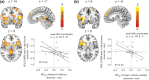
Physical exercise modulates food reward and helps control body weight. The endogenous µ-opioid receptor (MOR) system is involved in rewarding aspects of both food and physical exercise, yet interaction between endogenous opioid release following exercise and anticipatory food reward remains unresolved. Here we tested whether exercise-induced opioid release correlates with increased anticipatory reward processing in humans. We scanned 24 healthy lean men after rest and after a 1 h session of aerobic exercise with positron emission tomography (PET) using MOR-selective radioligand [11 C]carfentanil. After both PET scans, the subjects underwent a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) experiment where they viewed pictures of palatable versus nonpalatable foods to trigger anticipatory food reward responses. Exercise-induced changes in MOR binding in key regions of reward circuit (amygdala, thalamus, ventral and dorsal striatum, and orbitofrontal and cingulate cortices) were used to predict the changes in anticipatory reward responses in fMRI. Exercise-induced changes in MOR binding correlated negatively with the exercise-induced changes in neural anticipatory food reward responses in orbitofrontal and cingulate cortices, insula, ventral striatum, amygdala, and thalamus: higher exercise-induced opioid release predicted higher brain responses to palatable versus nonpalatable foods. We conclude that MOR activation following exercise may contribute to the considerable interindividual variation in food craving and consumption after exercise, which might promote compensatory eating and compromise weight control.
Keywords: brain imaging; food reward; opioid release; physical exercise.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
μ-opioid receptor system mediates reward processing in humans.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 16;9(1):1500. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03848-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29662095 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic Fitness Is Associated with Cerebral μ-Opioid Receptor Activation in Healthy Humans.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022 Jul 1;54(7):1076-1084. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002895. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022. PMID: 35195103
-
Opioid Release after High-Intensity Interval Training in Healthy Human Subjects.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jan;43(2):246-254. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.148. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28722022 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the opioid system in binge eating disorder.CNS Spectr. 2015 Dec;20(6):537-45. doi: 10.1017/S1092852915000668. Epub 2015 Oct 26. CNS Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26499083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine and opioid systems adaptation in alcoholism revisited: Convergent evidence from positron emission tomography and postmortem studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Nov;106:141-164. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 30243576
Cited by
-
A Survey of Molecular Imaging of Opioid Receptors.Molecules. 2019 Nov 19;24(22):4190. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224190. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31752279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is There a Role for GPCR Agonist Radiotracers in PET Neuroimaging?Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Oct 18;12:255. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00255. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31680859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A red nucleus-VTA glutamate pathway underlies exercise reward and the therapeutic effect of exercise on cocaine use.Sci Adv. 2022 Sep 2;8(35):eabo1440. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo1440. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36054363 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of a 12-Month Weight Loss Intervention on Cognitive Outcomes in Adults with Overweight and Obesity.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 29;12(10):2988. doi: 10.3390/nu12102988. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33003548 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations associated with μ-opioid and dopamine receptor distributions in the central nervous system after high-intensity exercise bouts.Front Neuroimaging. 2024 Feb 22;3:1332384. doi: 10.3389/fnimg.2024.1332384. eCollection 2024. Front Neuroimaging. 2024. PMID: 38455686 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cambridge, V. C. , Ziauddeen, H. , Nathan, P. J. , Subramaniam, N. , Dodds, C. , Chamberlain, S. R. , … Fletcher, P. C. (2013). Neural and behavioral effects of a novel mu opioid receptor antagonist in binge‐eating obese people. Biological Psychiatry, 73(9), 887–894. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.10.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colasanti, A. , Searle, G. E. , Long, C. J. , Hill, S. P. , Reiley, R. R. , Quelch, D. , … Rabiner, E. A. (2012). Endogenous opioid release in the human brain reward system induced by acute amphetamine administration. Biological Psychiatry, 72(5), 371–377. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.01.027 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

