Cathepsins: Proteases that are vital for survival but can also be fatal
- PMID: 29885636
- PMCID: PMC7172164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.148
Cathepsins: Proteases that are vital for survival but can also be fatal
Abstract
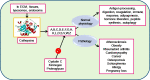
The state of enzymes in the human body determines the normal physiology or pathology, so all the six classes of enzymes are crucial. Proteases, the hydrolases, can be of several types based on the nucleophilic amino acid or the metal cofactor needed for their activity. Cathepsins are proteases with serine, cysteine, or aspartic acid residues as the nucleophiles, which are vital for digestion, coagulation, immune response, adipogenesis, hormone liberation, peptide synthesis, among a litany of other functions. But inflammatory state radically affects their normal roles. Released from the lysosomes, they degrade extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen and elastin, mediating parasite infection, autoimmune diseases, tumor metastasis, cardiovascular issues, and neural degeneration, among other health hazards. Over the years, the different types and isoforms of cathepsin, their optimal pH and functions have been studied, yet much information is still elusive. By taming and harnessing cathepsins, by inhibitors and judicious lifestyle, a gamut of malignancies can be resolved. This review discusses these aspects, which can be of clinical relevance.
Keywords: Carcinogenesis; Cathepsin; Extracellular matrix; Immune activation; Inflammation; Inhibitors.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Gasteiger E., Gattiker A., Hoogland C., Ivanyi I., Appel R.D., Bairoch A. ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3784–3788. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=168970&tool=pm... (Accessed 30 May 2015) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

