Effect of lipid and cellulose based matrix former on the release of highly soluble drug from extruded/spheronized, sintered and compacted pellets
- PMID: 29885655
- PMCID: PMC5994249
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-018-0783-8
Effect of lipid and cellulose based matrix former on the release of highly soluble drug from extruded/spheronized, sintered and compacted pellets
Abstract
Background: The study was to develop an extended release (ER) encapsulated and compacted pellets of Atenolol using hydrophobic (wax based and polymeric based) and high viscosity grade hydrophilic matrix formers to control the release of this highly water soluble drug by extrusion/spheronization (ES). Atenolol is used for cardiovascular diseases and available as an immediate release (IR) tablet dosage form. The lipids, Carnauba wax (CW), Glyceryl monostearate (GMS) and cellulose based i.e. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and Ethyl cellulose (EC) were used in preparing Atenolol ER pellets. Thermal sintering and compaction techniques were also applied to control the burst release of Atenolol.
Method: For this purpose, thirty-six trial formulations (F1-F36) were designed by Response Surface Methodology (RSM), using Design-Expert 10 software, keeping (HPMC K4M, K15 M & K100 M), (EC 7FP, 10FP & 100FP), waxes (GMS, & CW), their combinations, sintering temperature and duration, as input variables. Dissolution studies were performed in pH, 1.2, 4.5 and 6.8 dissolution media. Drug release kinetics using different models such as zero order, first order, Korsmeyer-Peppas, Hixon Crowell, Baker-Lonsdale and Higuchi kinetics were studied with the help of DDsolver, an excel based add-in program.
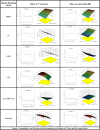
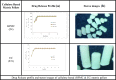
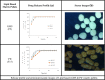
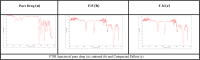
Results: The formulations F35 and F36 showed compliance with Korsmeyer-Peppas Super case II transport model (R2 = 0.975-0.971) in dissolution medium pH 4.5. No drug excipient interaction observed by FTIR. Stereomicroscopy showed that sintered combination pellets, (F35), were highly spherical (AR = 1.061, and sphericity = 0.943). The cross-sectional SEM magnification (at 7000X) of F34 and F35 showed dense cross-linking. The results revealed that the optimized formulations were F35 (sintered pellets) and F36 (compacted pellets) effectively controlling the drug release for 12 h.
Conclusion: Extended-release encapsulated, and compacted pellets were successfully prepared after the combination of lipids CW (10%) and GMS (20%) with EC (10FP 20% & 100FP 20%). Sintering and compaction, in addition, stabilized the system and controlled the initial burst release of the drug. Extended release (ER) Atenolol is an effective alternative of IR tablets in controlling hypertension and treating other cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Atenolol; Carnauba wax (CW); Ethyl cellulose (EC); Extended release; Extrusion-Spheronization; Fourier transform spectroscopy (FTIR); Glyceryl monostearate (GMS); Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC); Pellets; Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipids bearing extruded-spheronized pellets for extended release of poorly soluble antiemetic agent-Meclizine HCl.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Apr 12;16(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0466-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28403892 Free PMC article.
-
QbD-based formulation development and evaluation of lipid-cellulose-based extended-release multi-particulates of cinitapride and its in-silico PBPK modeling.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;306(Pt 1):141388. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141388. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39988163
-
Development and Quality evaluation of sustained release pellets of eperisone HCl.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2021 Jan;34(1(Supplementary)):225-235. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34275846
-
A Review on Enteric Coated Pellets Composed of Core Pellets Prepared by Extrusion-Spheronization.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2019;13(2):83-90. doi: 10.2174/1872211313666190212115139. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2019. PMID: 30747090 Review.
-
[Development of Novel Functional Formulations Based on Pharmaceutical Technologies].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(3):419-435. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00183. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30828022 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Poly(Acrylic Acid)-Modified MoS2 Nanoparticle-Based Transdermal Delivery of Atenolol.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Aug 4;15:5517-5526. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S257906. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32801703 Free PMC article.
-
Statistically Optimized Polymeric Buccal Films of Eletriptan Hydrobromide and Itopride Hydrochloride: An In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1551. doi: 10.3390/ph16111551. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004417 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced gastric residence time of acyclovir by floating raft formulation using box-behnken design.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 7;10(2):e24301. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24301. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293518 Free PMC article.
-
Premium ethylcellulose polymer based architectures at work in drug delivery.Int J Pharm X. 2019 Jul 8;1:100023. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2019.100023. eCollection 2019 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2019. PMID: 31517288 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated vitamin E-coated polymer hybrid nanoplatform: A lucrative option for an enhanced in vitro macrophage retention for an anti-hepatitis B therapeutic prospect.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 10;15(1):e0227231. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227231. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31923260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Remington: The Science and Practice of Pharmacy 20th edn: Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science; 2000.
-
- Dixit N, Maurya SD, Sagar BP. Sustained release drug delivery system. Indian J Res Pharm Biotechnol. 2013;1:305.
-
- Quadir MA, Rahman MS, Karim MZ, Akter S, Awkat M, Reza M. Evaluation of hydrophobic materials as matrices for controlled-release drug delivery. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2003;16:17–28. - PubMed
-
- Zhou F, Vervaet C, Remon JP. Matrix pellets based on the combination of waxes, starches and maltodextrins. Int J Pharm. 1996;133:155–160. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(95)04431-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

