APOL1: The Balance Imposed by Infection, Selection, and Kidney Disease
- PMID: 29886044
- PMCID: PMC6101980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.05.008
APOL1: The Balance Imposed by Infection, Selection, and Kidney Disease
Abstract
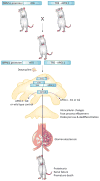
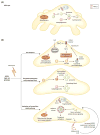
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects millions of people and constitutes a major health and financial burden worldwide. People of African descent are at an increased risk of developing kidney disease, which is mostly explained by two variants in the Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) gene that are found only in people of west African origin. It is hypothesized that these variants were genetically selected due to the protection they afford against African sleeping sickness, caused by the parasite Trypanosoma brucei. Targeting mutant APOL1 could have substantial therapeutic potential for treating kidney disease. In this review, we will describe the intriguing interplay between microbiology, genetics, and kidney disease as revealed in APOL1-associated kidney disease, discuss APOL1-induced cytotoxicity and its therapeutic implications.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein 1; chronic kidney disease; genetics.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct APOL1 functions in trypanosomes and kidney podocytes.Trends Parasitol. 2022 Feb;38(2):104-108. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Trends Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 34887168
-
The Cell Biology of APOL1.Semin Nephrol. 2017 Nov;37(6):538-545. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2017.07.007. Semin Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 29110761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein-L1 (APOL1): From Sleeping Sickness to Kidney Disease.Cells. 2024 Oct 20;13(20):1738. doi: 10.3390/cells13201738. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39451256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APOL1 renal risk variants have contrasting resistance and susceptibility associations with African trypanosomiasis.Elife. 2017 May 24;6:e25461. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25461. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28537557 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) cation current in HEK-293 cells and in human podocytes.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Mar;475(3):323-341. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02767-8. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 36449077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
APOL1-G2 accelerates nephrocyte cell death by inhibiting the autophagy pathway.Dis Model Mech. 2023 Dec 1;16(12):dmm050223. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050223. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 37969018 Free PMC article.
-
The function of apolipoproteins L (APOLs): relevance for kidney disease, neurotransmission disorders, cancer and viral infection.FEBS J. 2021 Jan;288(2):360-381. doi: 10.1111/febs.15444. Epub 2020 Jun 25. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32530132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenome-wide analysis reveals epistatic associations between APOL1 variants and chronic kidney disease and multiple other disorders.EBioMedicine. 2024 Mar;101:105000. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105000. Epub 2024 Feb 14. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38360481 Free PMC article.
-
Podocyte Sphingolipid Signaling in Nephrotic Syndrome.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Apr 17;55(S4):13-34. doi: 10.33594/000000356. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33861526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics and ESKD Disparities in African Americans.Am J Kidney Dis. 2019 Dec;74(6):811-821. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019. PMID: 31606237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Chronic Kidney Disease Surveillence System-United States.
-
- Hsu CY, et al. Racial differences in the progression from chronic renal insufficiency to end-stage renal disease in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(11):2902–7. - PubMed
-
- Kruzel-Davila E, Wasser WG, Skorecki K. APOL1 Nephropathy: A Population Genetics and Evolutionary Medicine Detective Story. Semin Nephrol. 2017;37(6):490–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

