Central regulation of energy metabolism by estrogens
- PMID: 29886181
- PMCID: PMC6066788
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.05.012
Central regulation of energy metabolism by estrogens
Abstract
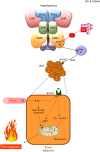
Background: Estrogenic actions in the brain prevent obesity. Better understanding of the underlying mechanisms may facilitate development of new obesity therapies.
Scope of review: This review focuses on the critical brain regions that mediate effects of estrogens on food intake and/or energy expenditure, the molecular signals that are involved, and the functional interactions between brain estrogens and other signals modulating metabolism. Body weight regulation by estrogens in male brains will also be discussed.
Major conclusions: 17β-estradiol acts in the brain to regulate energy homeostasis in both sexes. It can inhibit feeding and stimulate brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. A better understanding of the central actions of 17β-estradiol on energy balance would provide new insight for the development of therapies against obesity in both sexes.
Keywords: Brown adipose tissue; Energy balance; Estrogens; Food intake; Hypothalamus; Metabolism; Obesity.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez M., Tena-Sempere M. Estrogens and the control of energy homeostasis: a brain perspective. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2015;26:411–421. - PubMed
-
- Flegal K.M., Carroll M.D., Ogden C.L., Curtin L.R. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2010;303:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Billeci A.M., Paciaroni M., Caso V., Agnelli G. Hormone replacement therapy and stroke. Current Vascular Pharmacology. 2008;6:112–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

