Scaffold attachment factor B suppresses HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T cells by preventing binding of RNA polymerase II to HIV-1's long terminal repeat
- PMID: 29887524
- PMCID: PMC6078458
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002018
Scaffold attachment factor B suppresses HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T cells by preventing binding of RNA polymerase II to HIV-1's long terminal repeat
Abstract
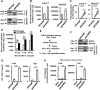
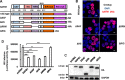
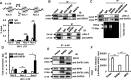
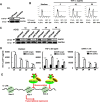
The 5' end of the HIV, type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat (LTR) promoter plays an essential role in driving viral transcription and productive infection. Multiple host and viral factors regulate LTR activity and modulate HIV-1 latency. Manipulation of the HIV-1 LTR provides a potential therapeutic strategy for combating HIV-1 persistence. In this study, we identified an RNA/DNA-binding protein, scaffold attachment factor B (SAFB1), as a host cell factor that represses HIV-1 transcription. We found that SAFB1 bound to the HIV-1 5' LTR and significantly repressed 5' LTR-driven viral transcription and HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T cells. Mechanistically, SAFB1-mediated repression of HIV-1 transcription and infection was independent of its RNA- and DNA-binding capacities. Instead, by binding to phosphorylated RNA polymerase II, SAFB1 blocked its recruitment to the HIV-1 LTR. Of note, SAFB1-mediated repression of HIV-1 transcription from proviral DNA maintained HIV-1 latency in CD4+ T cells. In summary, our findings reveal that SAFB1 binds to the HIV-1 LTR and physically interacts with phosphorylated RNA polymerase II, repressing HIV-1 transcription initiation and elongation. Our findings improve our understanding of host modulation of HIV-1 transcription and latency and provide a new host cell target for improved anti-HIV-1 therapies.
Keywords: HIV; host–pathogen interaction; viral transcription; virology; virus.
© 2018 Ma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health
Figures

Similar articles
-
X-Linked RNA-Binding Motif Protein Modulates HIV-1 Infection of CD4+ T Cells by Maintaining the Trimethylation of Histone H3 Lysine 9 at the Downstream Region of the 5' Long Terminal Repeat of HIV Proviral DNA.mBio. 2020 Apr 21;11(2):e03424-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03424-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32317327 Free PMC article.
-
Naf1 Regulates HIV-1 Latency by Suppressing Viral Promoter-Driven Gene Expression in Primary CD4+ T Cells.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01830-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01830-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795436 Free PMC article.
-
Semen Exosomes Promote Transcriptional Silencing of HIV-1 by Disrupting NF-κB/Sp1/Tat Circuitry.J Virol. 2018 Oct 12;92(21):e00731-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00731-18. Print 2018 Nov 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30111566 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Non-Epigenetic Activation of HIV Latency through the T-Cell Receptor Signalosome.Viruses. 2020 Aug 8;12(8):868. doi: 10.3390/v12080868. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32784426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAFB1- and SAFB2-mediated transcriptional repression: relevance to cancer.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Aug;40(4):826-30. doi: 10.1042/BST20120030. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22817742 Review.
Cited by
-
Tryptophan Metabolism Activates Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Pathway To Promote HIV-1 Infection and Reactivation.mBio. 2019 Dec 17;10(6):e02591-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02591-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31848275 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 releases epigenetic silencing of HIV-1 replication by displacing the polycomb repressive complex 2 from binding to the LTR promoter.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 8;47(6):3013-3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz117. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30788509 Free PMC article.
-
X-Linked RNA-Binding Motif Protein Modulates HIV-1 Infection of CD4+ T Cells by Maintaining the Trimethylation of Histone H3 Lysine 9 at the Downstream Region of the 5' Long Terminal Repeat of HIV Proviral DNA.mBio. 2020 Apr 21;11(2):e03424-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03424-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32317327 Free PMC article.
-
The CREB Regulated Transcription Coactivator 2 Suppresses HIV-1 Transcription by Preventing RNA Pol II from Binding to HIV-1 LTR.Virol Sin. 2021 Aug;36(4):796-809. doi: 10.1007/s12250-021-00363-1. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Virol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33723808 Free PMC article.
-
PIWIL4 Maintains HIV-1 Latency by Enforcing Epigenetically Suppressive Modifications on the 5' Long Terminal Repeat.J Virol. 2020 May 4;94(10):e01923-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01923-19. Print 2020 May 4. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32161174 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

