Multifunctional mussel-inspired copolymerized epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)/arginine coating: the potential as an ad-layer for vascular materials
- PMID: 29887988
- PMCID: PMC5987673
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbw027
Multifunctional mussel-inspired copolymerized epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)/arginine coating: the potential as an ad-layer for vascular materials
Abstract
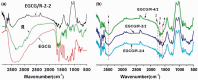
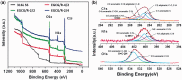
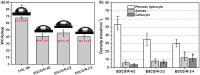
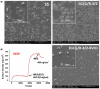
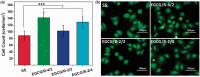
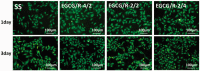
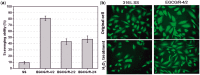
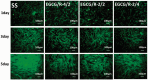
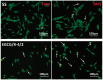
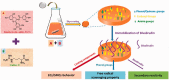
Surface properties are considered to be important factors in addressing proper functionalities. In this paper, a multifunctional mussel-inspired coating was prepared via the direct copolymerization of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and arginine. The coating formation was confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectra. The EGCG/arginine coating contained diverse functional groups like amines, phenols and carboxyls, whose densities were also tunable. Such mussel-inspired coating could also be applied as an ad-layer for its secondary reactivity, demonstrated by quartz crystal microbalance technique. Moreover, the tunable surface density of phenols showed potential ability in modulating endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell viability. The coatings rich in phenols presented excellent free radical scavenging property. Current results strongly indicated the potential of EGCG/arginine coatings to be applied as an ad-layer for vascular materials.
Keywords: Mussel chemistry; epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG); multifunction; surface modification; vascular devices.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The behavior of vascular smooth muscle cells and platelets onto epigallocatechin gallate-releasing poly(l-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) as stent-coating materials.Biomaterials. 2008 Mar;29(7):884-93. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.10.052. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Biomaterials. 2008. PMID: 18031806
-
Epigallocatechin gallate mediated sandwich-like coating for mimicking endothelium with sustained therapeutic nitric oxide generation and heparin release.Biomaterials. 2021 Feb;269:120418. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120418. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Biomaterials. 2021. PMID: 33143876
-
Polycaprolactone vascular graft with epigallocatechin gallate embedded sandwiched layer-by-layer functionalization for enhanced antithrombogenicity and anti-inflammation.J Control Release. 2020 Apr 10;320:226-238. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.043. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 31982435
-
Green Tea Polyphenol Induced Mg2+-rich Multilayer Conversion Coating: Toward Enhanced Corrosion Resistance and Promoted in Situ Endothelialization of AZ31 for Potential Cardiovascular Applications.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Nov 6;11(44):41165-41177. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b17221. Epub 2019 Oct 25. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31651138
-
Phospholipid-based multifunctional coating via layer-by-layer self-assembly for biomedical applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Nov;116:111237. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111237. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32806322
References
-
- Davignon J, Ganz P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004;109:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Dangas GD, Claessen BE, Caixeta A, et al. In-stent restenosis in the drug-eluting stent era. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;56:1897–907. - PubMed
-
- Kleiner LW, Wright JC, Wang Y. Evolution of implantable and insertable drug delivery systems. J Control Release 2014;181:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Papafaklis MI, Chatzizisis YS, Naka KK, et al. Drug-eluting stent restenosis: effect of drug type, release kinetics, hemodynamics and coating strategy. Pharmacol Ther 2012;134:43–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

