D-GENIES: dot plot large genomes in an interactive, efficient and simple way
- PMID: 29888139
- PMCID: PMC5991294
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4958
D-GENIES: dot plot large genomes in an interactive, efficient and simple way
Abstract
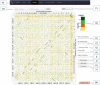
Dot plots are widely used to quickly compare sequence sets. They provide a synthetic similarity overview, highlighting repetitions, breaks and inversions. Different tools have been developed to easily generated genomic alignment dot plots, but they are often limited in the input sequence size. D-GENIES is a standalone and web application performing large genome alignments using minimap2 software package and generating interactive dot plots. It enables users to sort query sequences along the reference, zoom in the plot and download several image, alignment or sequence files. D-GENIES is an easy-to-install, open-source software package (GPL) developed in Python and JavaScript. The source code is available at https://github.com/genotoul-bioinfo/dgenies and it can be tested at http://dgenies.toulouse.inra.fr/.
Keywords: Dot plot; Genome assessment; Interactive user interface; Large genomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

