Diagnostic accuracy of image-guided biopsies in small (<4 cm) renal masses with implications for active surveillance: a systematic review of the evidence
- PMID: 29888978
- PMCID: PMC6350473
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20170761
Diagnostic accuracy of image-guided biopsies in small (<4 cm) renal masses with implications for active surveillance: a systematic review of the evidence
Abstract
Objective:: To determine the safety and diagnostic accuracy of renal tumour biopsies in a defined population of small renal masses (SRMs) only <4 cm using 3 × 2 table, intention to diagnose approach. 3 × 2 table approach examines indeterminate results as a separate category rather than pushing these through traditional 2 × 2 table (four-cell matrix) approach.
Methods:: A highly sensitive search was performed in the Cochrane Library, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects; MEDLINE and MEDLINE in Process, EMBASE and conference proceedings (1966-2016) for the acquisition of data on the diagnostic accuracy and complications of RTB in patients with SRM <4 cm. Methodological quality and risk of bias was assessed using QUADAS-2. Test characteristics were calculated using conventional 2 × 2 contingency table analysis excluding non-diagnostic biopsies, and an intention-to-diagnose approach with a 3 × 2 table for pooled estimates of the sensitivity and specificity.
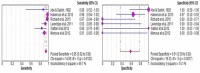
Results:: A total of 20 studies were included with a total sample size of 974. The pooled estimates for sensitivity and specificity of RTB based upon univariate analysis using 2 × 2 table observed sensitivity 0.952 [confidence interval (CI) 0.908-0.979] and specificity 0.824 (CI 0.566-0.962). Using the 3 × 2 table and intention-to-diagnose principle, sensitivity 0.947 (CI 0.925-0.965) and specificity 0.609 (CI 0.385-0.803) decreased.
Conclusion:: RTB in SRMs (<4 cm) is associated with a high diagnostic sensitivity but poor specificity when non-diagnostic results are included by a 3 × 2 table for analysis (intention to diagnose approach). Risk of non-diagnostic results and poor quality of research need addressing through future studies, preferably by a well-designed prospective study appropriately powered for diagnostic accuracy using valid reference standards.
Advances in knowledge:: A comprehensive synthesis of literature on image-guided biopsies in SRMs using a different methodology and study design.
Figures


References
-
- Volpe A, Terrone C, Scarpa RM. The current role of percutaneous needle biopsies of renal tumours. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2009; 81: 107–12. - PubMed
-
- Abel EJ, Culp SH, Matin SF, Tamboli P, Wallace MJ, Jonasch E, et al. . Percutaneous biopsy of primary tumor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma to predict high risk pathological features: comparison with nephrectomy assessment. J Urol 2010; 184: 1877–81. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.06.105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

