Nonprimary Maternal Cytomegalovirus Infection After Viral Shedding in Infants
- PMID: 29889809
- PMCID: PMC6016842
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0000000000001877
Nonprimary Maternal Cytomegalovirus Infection After Viral Shedding in Infants
Abstract
Background: Most infants with congenital Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection are born to seropositive women as a result of maternal CMV nonprimary infection (reinfection or reactivation). Although infected children are known to transmit CMV to their seronegative mothers, the frequency and magnitude of nonprimary maternal CMV infection after exposure to viral shedding by children in their household have not been characterized.
Methods: A cohort of Ugandan newborns and their mothers were tested weekly for CMV by quantitative polymerase chain reaction of oral swabs. Infant primary infection and maternal nonprimary infection were defined by the onset of persistent high-level oral CMV shedding. Strain-specific antibody testing was used to assess maternal reinfection. Cox regression models with time-dependent covariates were used to evaluate risk factors for nonprimary maternal infection.
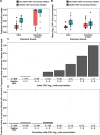
Results: Nonprimary CMV infection occurred in 15 of 30 mothers, all after primary infection of their infants by a median of 6 weeks (range: 1-10) in contrast to none of the mothers of uninfected infants. The median duration of maternal oral shedding lasted 18 weeks (range: 4-42) reaching a median maximum viral load of 4.69 log copies/mL (range: 3.22-5.64). Previous-week infant CMV oral quantities strongly predicted maternal nonprimary infection (hazard ratio: 2.32 per log10 DNA copies/swab increase; 95% confidence interval: 1.63-3.31). Maternal nonprimary infections were not associated with changes in strain-specific antibody responses.
Conclusions: Nonprimary CMV infection was common in mothers after primary infection in their infants, consistent with infant-to-mother transmission. Because infants frequently acquire CMV from their mothers, for example, through breast milk, this suggests the possibility of "ping-pong" infections. Additional research is needed to characterize the antigenic and genotypic strains transmitted among children and their mothers.
Figures
References
-
- Dollard SC, Grosse SD, Ross DS. New estimates of the prevalence of neurological and sensory sequelae and mortality associated with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Rev Med Virol. 2007;17:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Larke RP, Wheatley E, Saigal S, Chernesky MA. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in an urban Canadian community. J Infect Dis. 1980;142:647–653. - PubMed
-
- de Vries JJ, van Zwet EW, Dekker FW, Kroes AC, Verkerk PH, Vossen AC. The apparent paradox of maternal seropositivity as a risk factor for congenital cytomegalovirus infection: a population-based prediction model. Rev Med Virol. 2013;23:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Boppana SB, Fowler KB, Britt WJ, Stagno S, Pass RF. Symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection in infants born to mothers with preexisting immunity to cytomegalovirus. Pediatrics. 1999;104:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Ljungman P, Griffiths P, Paya C. Definitions of cytomegalovirus infection and disease in transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:1094–1097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

