14-3-3: A Case Study in PPI Modulation
- PMID: 29890630
- PMCID: PMC6099619
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23061386
14-3-3: A Case Study in PPI Modulation
Abstract
In recent years, targeting the complex network of protein⁻protein interactions (PPIs) has been identified as a promising drug-discovery approach to develop new therapeutic strategies. 14-3-3 is a family of eukaryotic conserved regulatory proteins which are of high interest as potential targets for pharmacological intervention in human diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative and metabolic disorders. This viewpoint is built on the “hub” nature of the 14-3-3 proteins, binding to several hundred identified partners, consequently implicating them in a multitude of different cellular mechanisms. In this review, we provide an overview of the structural and biological features of 14-3-3 and the modulation of 14-3-3 PPIs for discovering small molecular inhibitors and stabilizers of 14-3-3 PPIs.
Keywords: 14-3-3 PPIs; PPI modulation; small molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

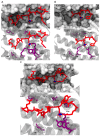




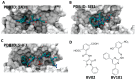
References
-
- Moore B.W., Perez V.J., Carlson F.D., editors. Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Nervous Integration. Prentice-Hall Inc.; The Marine Biological Laboratory; Woods Hole, MA, USA: 1967. pp. 343–359.
-
- Ichimura T., Isobe T., Okuyama T., Takahashi N., Araki K., Kuwano R., Takahashi Y. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for brain-specific 14-3-3 protein, a protein kinase-dependent activator of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1988;85:7084–7088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7084. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

