Dysregulated HAI-2 Plays an Important Role in Renal Cell Carcinoma Bone Metastasis through Ligand-Dependent MET Phosphorylation
- PMID: 29890660
- PMCID: PMC6025049
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10060190
Dysregulated HAI-2 Plays an Important Role in Renal Cell Carcinoma Bone Metastasis through Ligand-Dependent MET Phosphorylation
Abstract
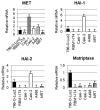
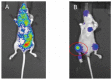
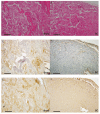
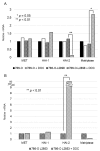
MET, a c-met proto-oncogene product and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) receptor, is known to play an important role in cancer progression, including bone metastasis. In a previous study, we reported increased expression of MET and matriptase, a novel activator of HGF, in bone metastasis. In this study, we employed a mouse model of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) bone metastasis to clarify the significance of the HGF/MET signaling axis and the regulator of HGF activator inhibitor type-2 (HAI-2). Luciferase-transfected 786-O cells were injected into the left cardiac ventricle of mice to prepare the mouse model of bone metastasis. The formation of bone metastasis was confirmed by whole-body bioluminescent imaging, and specimens were extracted. Expression of HGF/MET-related molecules was analyzed. Based on the results, we produced HAI-2 stable knockdown 786-O cells, and analyzed invasiveness and motility. Expression of HGF and matriptase was increased in bone metastasis compared with the control, while that of HAI-2 was decreased. Furthermore, we confirmed increased phosphorylation of MET in bone metastasis. The expression of matriptase was upregulated, and both invasiveness and motility were increased significantly by knockdown of HAI-2. The significance of ligand-dependent MET activation in RCC bone metastasis is considered, and HAI-2 may be an important regulator in this system.
Keywords: HAI-2; HGF; MET; RCC; bone metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysregulation of Type II Transmembrane Serine Proteases and Ligand-Dependent Activation of MET in Urological Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 11;21(8):2663. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082663. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32290402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matriptase-Induced Phosphorylation of MET is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Invasive Bladder Cancer; an Immunohistochemical Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 22;19(12):3708. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123708. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30469509 Free PMC article.
-
Possible role of combined therapy targeting MET and pro-HGF activation for renal cell carcinoma: analysis by human HGF-producing SCID mice.Hum Cell. 2023 Mar;36(2):775-785. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-00857-y. Epub 2023 Jan 28. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36708441
-
Clinical relevance of hepsin and hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 2 expression in renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2007 Apr;98(4):491-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00412.x. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Cancer Sci. 2007. PMID: 17309599 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor activation inhibitors - therapeutic potential in cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010 Jan;10(1):47-57. doi: 10.2174/1871520611009010047. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20015004 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the HGF/MET Axis in Cancer Therapy: Challenges in Resistance and Opportunities for Improvement.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 6;8:152. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00152. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32435640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Renal Cell Tumors.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;11(2):206. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11020206. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33573278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor overexpression promotes osteoclastogenesis and exacerbates bone loss in CIA mice.J Orthop Translat. 2020 Dec 10;27:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2020.10.011. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2020. PMID: 33344167 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Type II Transmembrane Serine Proteases and Ligand-Dependent Activation of MET in Urological Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 11;21(8):2663. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082663. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32290402 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rini B.I., Halabi S., Rosenberg J.E., Stadler W.M., Vaena D.A., Ou S.S., Archer L., Atkins J.N., Picus J., Czaykowski P., et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Calgb 90206. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:5422–5428. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.9847. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Patil S., Figlin R.A., Hutson T.E., Michaelson M.D., Negrier S., Kim S.T., Huang X., Motzer R.J. Prognostic factors for progression-free and overall survival with sunitinib targeted therapy and with cytokine as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2011;22:295–300. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq342. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

