Synthesis of 2-Mercapto-(2-Oxoindolin-3-Ylidene)Acetonitriles from 3-(4-Chloro-5 H-1,2,3-Dithiazol-5-Ylidene)Indolin-2-ones
- PMID: 29890669
- PMCID: PMC6100569
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23061390
Synthesis of 2-Mercapto-(2-Oxoindolin-3-Ylidene)Acetonitriles from 3-(4-Chloro-5 H-1,2,3-Dithiazol-5-Ylidene)Indolin-2-ones
Abstract
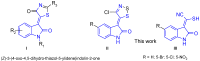
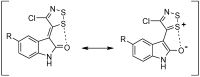
Alkylidene oxindoles are important functional moieties and building blocks in pharmaceutical and synthetic chemistry. Our interest in biologically active compounds focused our studies on the synthesis of novel oxindoles, bearing on the exocyclic double bond at the C8, CN, and S groups. Extending the potential applications of Appel’s salt, we developed a new synthetic approach by investigating the reactions of C5-substituted 2-oxindoles with 4,5-dichloro-1,2,3-dithiazolium chloride (Appel’s salt) to give original (Z)-3-(4-chloro-5H-1,2,3-dithiazol-5-ylidene)indolin-2-one derivatives, and new 2-mercapto-(2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)acetonitriles via a dithiazole ring-opening reaction. The work described in this article represents further applications of Appel’s salt in the conception of novel heterocyclic rings, in an effort to access original bioactive compounds. Fifteen new compounds were prepared and fully characterized.
Keywords: 1,2,3-dithiazole; 3-alkenyl-2-oxindole; Appel’s salt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A Qualitative Comparison of the Reactivities of 3,4,4,5-Tetrachloro-4H-1,2,6-thiadiazine and 4,5-Dichloro-1,2,3-dithiazolium Chloride.Molecules. 2015 Aug 12;20(8):14576-94. doi: 10.3390/molecules200814576. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26274946 Free PMC article.
-
The Reaction of DABCO with 4-Chloro-5H-1,2,3-dithiazoles: Synthesis and Chemistry of 4-[N-(2-Chloroethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-5H-1,2,3-dithiazoles.J Org Chem. 2016 Jan 15;81(2):615-31. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02497. Epub 2015 Dec 24. J Org Chem. 2016. PMID: 26671065
-
Crystal Structure and Solid-State Packing of 4-Chloro-5H-1,2,3-dithiazol-5-one and 4-Chloro-5H-1,2,3-dithiazole-5-thione.Molecules. 2021 Sep 28;26(19):5875. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195875. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641419 Free PMC article.
-
[The chemistry of pericyclic reactions and their application to syntheses of heterocyclic compounds].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Sep;123(9):717-59. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.717. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14513766 Review. Japanese.
-
Literature Survey and Further Studies on the 3-Alkylation of N-Unprotected 3-Monosubstituted Oxindoles. Practical Synthesis of N-Unprotected 3,3-Disubstituted Oxindoles and Subsequent Transformations on the Aromatic Ring.Molecules. 2016 Dec 26;22(1):24. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010024. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 28035962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Cyclization of 4-(2-Aminophenyl)-4-oxo-2-phenylbutanenitriles into 2-(3-Oxoindolin-2-ylidene)acetonitriles.ACS Omega. 2022 Apr 15;7(16):14345-14356. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01238. eCollection 2022 Apr 26. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35573208 Free PMC article.
-
The Synthesis and Biological Applications of the 1,2,3-Dithiazole Scaffold.Molecules. 2023 Apr 3;28(7):3193. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073193. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weniger B., Jiang Y., Anton R., Bastida J., Varea T., Quirion J.-C. Oxindole Alkaloids from Neolaugeria Resinosa. Phytochemistry. 1993;32:1587–1590. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(93)85185-T. - DOI
-
- Millemaggi A., Perry A., Whitwood A.C., Taylor R.J.K. Telescoped Enolate Arylation/HWE Procedure for the Preparation of 3-Alkenyl-Oxindoles: The First Synthesis of Soulieotine. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009;18:2947–2952. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.200900294. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

