Predictors of atrial fibrillation in ibrutinib-treated CLL patients: a prospective study
- PMID: 29891001
- PMCID: PMC5996546
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-018-0626-0
Predictors of atrial fibrillation in ibrutinib-treated CLL patients: a prospective study
Abstract
Background: Ibrutinib is an oral irreversible inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase, indicated for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. The drug is generally well tolerated; however, not infrequent side effects are reported, with the major two being bleeding and ibrutinib-related atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation pathogenesis in this setting is not completely clear, and no prospective studies have evaluated the impact of previous cardiologic history and baseline characteristics.
Methods: We prospectively performed cardiologic assessment in 43 CLL patients before starting ibrutinib therapy. Cardiologic workup included comorbidity collection and electrocardiographic and echocardiographic baseline evaluation.
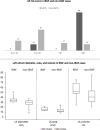
Results: After a median observation of 8 months, seven patients developed atrial fibrillation (16.3%). Cases developing atrial fibrillation were all elderly males (p = 0.04), and mostly with a history of previous arterial hypertension (p = 0.009). Atrial fibrillation occurrence also correlated with the presence of one or more pre-existent cardiologic comorbidities (p = 0.03), with a higher atrial fibrillation risk score (calculated with comorbidities and cardiologic risk factor evaluation p < 0.001), and with higher left atrial diameter (p = 0.02) and area (p = 0.03) by echocardiography. The occurrence of atrial fibrillation was managed after an integrated cardio-oncologic evaluation: anticoagulation was started in 4 (57.1%) patients and beta-blockers or amiodarone in 5 (71.4%). One patient underwent electric cardioversion and another patient pacemaker positioning to normalise heart rate in order to continue ibrutinib.
Conclusion: Our data show that echocardiography is a highly informative and reproducible tool that should be included in pre-treatment workup for patients who are candidates for ibrutinib therapy.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Cardio-oncology; Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; Ibrutinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The data collection on CLL patients had been approved by the local Ethical Committee and patients gave informed consent.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Wiczer TE, Levine LB, Brumbaugh J, Coggins J, Zhao Q, Ruppert AS, Rogers K, McCoy A, Mousa L, Guha A, Heerema NA, Maddocks K, Christian B, Andritsos LA, Jaglowski S, Devine S, Baiocchi R, Woyach J, Jones J, Grever M, Blum KA, Byrd JC, Awan FT. Cumulative incidence, risk factors, and management of atrial fibrillation in patients receiving ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2017;1:1739–1748. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thompson PA, Lévy V, Tam CS, Al Nawakil C, Goudot FX, Quinquenel A, Ysebaert L, Michallet AS, Dilhuydy MS, Van Den Neste E, Dupuis J, Keating MJ, Meune C, Cymbalista F. Atrial fibrillation in CLL patients treated with ibrutinib. An international retrospective study. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:462–466. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14324. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

