Acute hepatitis E superinfection leading to chronic hepatitis B reactivation
- PMID: 29891510
- PMCID: PMC6011448
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223616
Acute hepatitis E superinfection leading to chronic hepatitis B reactivation
Abstract
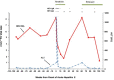
Reactivation of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) can be associated with significant morbidity and mortality. There are many different causes of hepatitis B reactivation. This case describes an Asian woman with stable CHB presenting with significant hepatitis flare with markedly elevated serum aminotransferases and hepatitis B virus DNA level. The clinical symptoms were subtle with fatigue and vague right upper quadrant tenderness. We ruled out drug-associated hepatotoxicity and screened for common causes of acute hepatitis. Interestingly, she was noted to have reactive anti-hepatitis E virus (HEV) IgM at initial presentation followed by anti-HEV IgG positivity a month later. The serological pattern confirmed the diagnosis of acute hepatitis E. The combination of antiviral therapy for hepatitis B and resolution of acute hepatitis E resulted in normalisation of serum aminotransferases. This case illustrates the importance of taking a careful history and having a high index of suspicion for various aetiologies when evaluating patients with reactivation of CHB.
Keywords: foodborne infections; hepatitis B; hepatitis other.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources