Model of the adaptive immune response system against HCV infection reveals potential immunomodulatory agents for combination therapy
- PMID: 29891859
- PMCID: PMC5995896
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27163-0
Model of the adaptive immune response system against HCV infection reveals potential immunomodulatory agents for combination therapy
Abstract
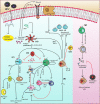
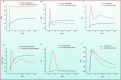
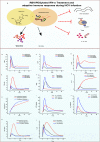
A regulated immune system employs multiple cell types, diverse variety of cytokines and interacting signalling networks against infections. Systems biology offers a promising solution to model and simulate such large populations of interacting components of immune systems holistically. This study focuses on the distinct components of the adaptive immune system and analysis, both individually and in association with HCV infection. The effective and failed adaptive immune response models have been developed followed by interventions/perturbations of various treatment strategies to get better assessment of the treatment responses under varying stimuli. Based on the model predictions, the NK cells, T regulatory cells, IL-10, IL-21, IL-12, IL-2 entities are found to be the most critical determinants of treatment response. The proposed potential immunomodulatory therapeutic interventions include IL-21 treatment, blocking of inhibitory receptors on T-cells and exogenous anti-IL-10 antibody treatment. The relative results showed that these interventions have differential effect on the expression levels of cellular and cytokines entities of the immune response. Notably, IL-21 enhances the expression of NK cells, Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and CD4+ T cells and hence restore the host immune potential. The models presented here provide a starting point for cost-effective analysis and more comprehensive modeling of biological phenomenon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Interferon-gamma: biologic functions and HCV terapy (type I/II) (2 of 2 parts).Clin Ter. 2006 Sep-Oct;157(5):457-68. Clin Ter. 2006. Retraction in: Clin Ter. 2008 May-Jun;159(3):208. PMID: 17147054 Retracted. Review.
-
[Immunology of HCV infection: the causes of impaired cellular immune response and the effect of antiviral treatment].Orv Hetil. 2006 Apr 2;147(13):591-600. Orv Hetil. 2006. PMID: 16623441 Hungarian.
-
Chronic hepatitis C in the advanced adult and elderly subjects.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009 Jun;55(2):145-57. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009. PMID: 19305374 Review.
-
Both Hepatitis C Virus-Specific T Cell Responses and IL28B rs12979860 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Genotype Influence Antihepatitis C Virus Treatment Outcome in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2017 Jun;37(6):278-286. doi: 10.1089/jir.2016.0078. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2017. PMID: 28440692
-
Direct-acting antiviral therapy enhances total CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells responses, but does not alter T-cells activation among HCV mono-infected, and HCV/HIV-1 co-infected patients.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018 Sep;42(4):319-329. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Dec 24. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29279268
Cited by
-
Nonthermal plasma as part of a novel strategy for vaccination.Plasma Process Polym. 2020 Oct;17(10):2000051. doi: 10.1002/ppap.202000051. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Plasma Process Polym. 2020. PMID: 32837491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Application of Exosomes in Vaccine Development and Delivery.Pharm Res. 2022 Nov;39(11):2635-2671. doi: 10.1007/s11095-021-03143-4. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35028802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: S100A8 as a Promising Biomarker Through Integrated RNA-Seq Analysis.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Dec 30;17:6199-6210. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S495121. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 39759083 Free PMC article.
-
Variations in killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor and human leukocyte antigen genes and immunity to malaria.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Aug;17(8):799-806. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0482-z. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32541835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Holistic View on the Structure of Immune Response: Petri Net Model.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 4;11(2):452. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020452. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830988 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

