Brain Cell Type Specific Gene Expression and Co-expression Network Architectures
- PMID: 29892006
- PMCID: PMC5995803
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27293-5
Brain Cell Type Specific Gene Expression and Co-expression Network Architectures
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Brain Cell Type Specific Gene Expression and Co-expression Network Architectures.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 24;11(1):19430. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97284-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34561470 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
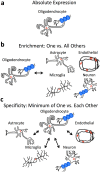
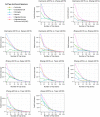
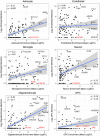
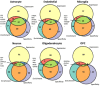
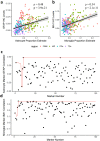
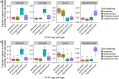
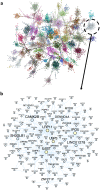
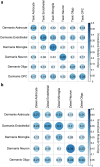
Elucidating brain cell type specific gene expression patterns is critical towards a better understanding of how cell-cell communications may influence brain functions and dysfunctions. We set out to compare and contrast five human and murine cell type-specific transcriptome-wide RNA expression data sets that were generated within the past several years. We defined three measures of brain cell type-relative expression including specificity, enrichment, and absolute expression and identified corresponding consensus brain cell "signatures," which were well conserved across data sets. We validated that the relative expression of top cell type markers are associated with proxies for cell type proportions in bulk RNA expression data from postmortem human brain samples. We further validated novel marker genes using an orthogonal ATAC-seq dataset. We performed multiscale coexpression network analysis of the single cell data sets and identified robust cell-specific gene modules. To facilitate the use of the cell type-specific genes for cell type proportion estimation and deconvolution from bulk brain gene expression data, we developed an R package, BRETIGEA. In summary, we identified a set of novel brain cell consensus signatures and robust networks from the integration of multiple datasets and therefore transcend limitations related to technical issues characteristic of each individual study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Swanson LW, Bota M. Foundational model of structural connectivity in the nervous system with a schema for wiring diagrams, connectome, and basic plan architecture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:20610–20617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015128107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gokhan S, et al. Combinatorial profiles of oligodendrocyte-selective classes of transcriptional regulators differentially modulate myelin basic protein gene expression. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2005;25:8311–8321. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1850-05.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG050986/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057440/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002876/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- RF1 AG054014/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003625/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 NS052738/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX002395/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R37 NS042925/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AG052261/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052411/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046170/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057907/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA008227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109677/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

