Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 29892015
- PMCID: PMC6136836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0133-9
Multi-ethnic genome-wide association study for atrial fibrillation
Abstract
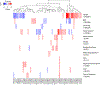
Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects more than 33 million individuals worldwide1 and has a complex heritability2. We conducted the largest meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for AF to date, consisting of more than half a million individuals, including 65,446 with AF. In total, we identified 97 loci significantly associated with AF, including 67 that were novel in a combined-ancestry analysis, and 3 that were novel in a European-specific analysis. We sought to identify AF-associated genes at the GWAS loci by performing RNA-sequencing and expression quantitative trait locus analyses in 101 left atrial samples, the most relevant tissue for AF. We also performed transcriptome-wide analyses that identified 57 AF-associated genes, 42 of which overlap with GWAS loci. The identified loci implicate genes enriched within cardiac developmental, electrophysiological, contractile and structural pathways. These results extend our understanding of the biological pathways underlying AF and may facilitate the development of therapeutics for AF.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests
Dr. Ellinor is the PI on a grant from Bayer to the Broad Institute focused on the genetics and therapeutics of atrial fibrillation. Dr. Psaty serves on the DSMB of a clinical trial funded by Zoll LifeCor and on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. Dr. Kirchhof receives research support from European Union, British Heart Foundation, Leducq Foundation, Medical Research Council (UK), and German Centre for Cardiovascular Research, from several drug and device companies active in atrial fibrillation, and has received honoraria from several such companies. Dr. Kirchhof is also listed as inventor on two patents held by University of Birmingham (Atrial Fibrillation Therapy WO 2015140571, Markers for Atrial Fibrillation WO 2016012783). Dr. Leineweber is an employee of Bayer. The genotyping of participants in the Broad AF Study and the expression analysis of left atrial tissue samples were supported by a grant from Bayer to the Broad Institute. Dr. Nazarian is a consultant to Biosense Webster, Siemens, and Cardiosolv. Dr. Nazarian also receives research grants from NIH/NHLBI, Siemens, Biosense Webster, and Imricor. S. Kathiresan has received grant support from Bayer and Amarin; holds equity in San Therapeutics and Catabasis; and has received personal fees for participation in scientific advisory boards for Catabasis, Regeneron Genetics Center, Merck, Celera, Genomics PLC, Corvidia Therapeutics, Novo Ventures. S. Kathiresan also received personal fees from consulting services from Novartis, AstraZeneca, Alnylam, Eli Lilly Company, Leerink Partners, Merck, Noble Insights, Bayer, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Novo Ventures, Haug Partners LLC. Genetic Modifiers Newco, Inc. Dr. Lubitz receives sponsored research support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, Biotronik, and Boehringer Ingelheim, and has consulted for St. Jude Medical / Abbott and Quest Diagnostics. The remaining authors have no disclosures.
Figures

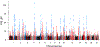

References
-
- January CT et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 64, (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG007417/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL139731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128914/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111314/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL127296/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 2014105/DDCF/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation/United States
- R01 HL116747/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092217/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HL123413/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 16EIA26410001/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- R01 HL090620/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

