Mutations in the SWI/SNF complex induce a targetable dependence on oxidative phosphorylation in lung cancer
- PMID: 29892061
- PMCID: PMC6650267
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0019-5
Mutations in the SWI/SNF complex induce a targetable dependence on oxidative phosphorylation in lung cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Mutations in the SWI/SNF complex induce a targetable dependence on oxidative phosphorylation in lung cancer.Nat Med. 2018 Oct;24(10):1627. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0173-9. Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 30104769
Abstract
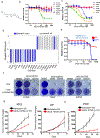
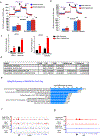
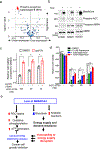
Lung cancer is a devastating disease that remains a top cause of cancer mortality. Despite improvements with targeted and immunotherapies, the majority of patients with lung cancer lack effective therapies, underscoring the need for additional treatment approaches. Genomic studies have identified frequent alterations in components of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex including SMARCA4 and ARID1A. To understand the mechanisms of tumorigenesis driven by mutations in this complex, we developed a genetically engineered mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma by ablating Smarca4 in the lung epithelium. We demonstrate that Smarca4 acts as a bona fide tumor suppressor and cooperates with p53 loss and Kras activation. Gene expression analyses revealed the signature of enhanced oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in SMARCA4 mutant tumors. We further show that SMARCA4 mutant cells have enhanced oxygen consumption and increased respiratory capacity. Importantly, SMARCA4 mutant lung cancer cell lines and xenograft tumors have marked sensitivity to inhibition of OXPHOS by a novel small molecule, IACS-010759, that is under clinical development. Mechanistically, we show that SMARCA4-deficient cells have a blunted transcriptional response to energy stress creating a therapeutically exploitable synthetic lethal interaction. These findings provide the mechanistic basis for further development of OXPHOS inhibitors as therapeutics against SWI/SNF mutant tumors.
Figures


References
-
- Wilson BG & Roberts CW SWI/SNF nucleosome remodellers and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 11, 481–492 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

