Analysis of Generalized Semiparametric Regression Models for Cumulative Incidence Functions with Missing Covariates
- PMID: 29892140
- PMCID: PMC5993453
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csda.2018.01.003
Analysis of Generalized Semiparametric Regression Models for Cumulative Incidence Functions with Missing Covariates
Abstract
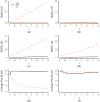
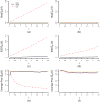
The cumulative incidence function quantifies the probability of failure over time due to a specific cause for competing risks data. The generalized semiparametric regression models for the cumulative incidence functions with missing covariates are investigated. The effects of some covariates are modeled as non-parametric functions of time while others are modeled as parametric functions of time. Different link functions can be selected to add flexibility in modeling the cumulative incidence functions. The estimation procedures based on the direct binomial regression and the inverse probability weighting of complete cases are developed. This approach modifies the full data weighted least squares equations by weighting the contributions of observed members through the inverses of estimated sampling probabilities which depend on the censoring status and the event types among other subject characteristics. The asymptotic properties of the proposed estimators are established. The finite-sample performances of the proposed estimators and their relative efficiencies under different two-phase sampling designs are examined in simulations. The methods are applied to analyze data from the RV144 vaccine efficacy trial to investigate the associations of immune response biomarkers with the cumulative incidence of HIV-1 infection.
Keywords: Competing risks; Inverse probability weighted complete-case; RV144 vaccine efficacy trial; Semiparametric regression model; Time-varying effects; Two-phase sampling.
Figures




References
-
- Cheng S, Fine J, Wei L. Prediction of cumulative incidence function under the proportional hazards model. Biometrics. 1988;54:219–228. - PubMed
-
- Cox D. Partial likelihood. Biometrika. 1975;62:269–276.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
