Declining trends of diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy with improving diabetes care indicators in Japanese patients with type 2 and type 1 diabetes (JDDM 46)
- PMID: 29892340
- PMCID: PMC5992467
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2018-000521
Declining trends of diabetic nephropathy, retinopathy and neuropathy with improving diabetes care indicators in Japanese patients with type 2 and type 1 diabetes (JDDM 46)
Abstract
Objective: We examined changes in prevalence of diabetic microvascular/macrovascular complications and diabetes care indicators for adults in Japan with type 2 and type 1 diabetes over one decade.
Research design and methods: Two independent cohorts were recruited with the same inclusion criteria in 2004 (cohort 1: 3319 with type 2 and 286 with type 1 diabetes) and in 2014 (cohort 2: 3932 with type 2 and 308 with type 1 diabetes). Prevalence of complications and care indicators including achieving treatment targets for glycemia, blood pressure, lipid control, body mass index (BMI), and smoking were compared. In addition, patients in cohort 1 were re-examined in 2014 and their data were compared with the baseline data of each cohort.
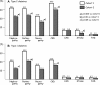
Results: In type 2 diabetes, the prevalence of nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, chronic kidney disease, current smoking and stroke significantly decreased, with improvements in achieving treatment target rates in cohort 2 two as compared with cohort 1. In type 1 diabetes, the prevalence of nephropathy, retinopathy, chronic kidney disease, and hemoglobin A1Cvalues significantly decreased. Decreases in prevalence of microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes were similarly found in each age-matched and sex-matched group, whereas younger patients exhibited marked increase in BMI and lower treatment target achieving rates compared with elderly patients. Regarding normoalbuminuric renal impairment, only a slight increase in the prevalence was observed both in type 2 and type 1 diabetes. In cohort 1, re-examined in 2014, care indicators were significantly improved from 2004, while complications increased with getting 10 years older.
Conclusions: We observed declining trends of diabetic microvascular complications with improvement in diabetes care indicators in type 2 and type 1 diabetes. Younger patients with type 2 diabetes exhibited marked increase in BMI and lower rates of achieving treatment targets compared with elderly patients, which remains a concern.
Keywords: diabetes care indicators; microvascular complications; nephropathy; type 1 diabetes; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, et al. Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;27(Suppl 1):S79–83. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources