Dietary and developmental shifts in butterfly-associated bacterial communities
- PMID: 29892359
- PMCID: PMC5990769
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.171559
Dietary and developmental shifts in butterfly-associated bacterial communities
Abstract
Bacterial communities associated with insects can substantially influence host ecology, evolution and behaviour. Host diet is a key factor that shapes bacterial communities, but the impact of dietary transitions across insect development is poorly understood. We analysed bacterial communities of 12 butterfly species across different developmental stages, using amplicon sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. Butterfly larvae typically consume leaves of a single host plant, whereas adults are more generalist nectar feeders. Thus, we expected bacterial communities to vary substantially across butterfly development. Surprisingly, only few species showed significant dietary and developmental transitions in bacterial communities, suggesting weak impacts of dietary transitions across butterfly development. On the other hand, bacterial communities were strongly influenced by butterfly species and family identity, potentially due to dietary and physiological variation across the host phylogeny. Larvae of most butterfly species largely mirrored bacterial community composition of their diets, suggesting passive acquisition rather than active selection. Overall, our results suggest that although butterflies harbour distinct microbiomes across taxonomic groups and dietary guilds, the dramatic dietary shifts that occur during development do not impose strong selection to maintain distinct bacterial communities across all butterfly hosts.
Keywords: diet; insect; metamorphosis; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
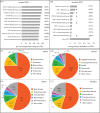


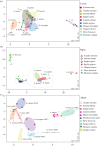
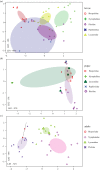
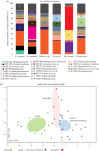

References
-
- McFall-Ngai MJ. 2002. Unseen forces: the influence of bacteria on animal development. Dev. Biol. 242, 1–14. (doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0522) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fraune S, Bosch TCG. 2010. Why bacteria matter in animal development and evolution. Bioessays 32, 571–580. (doi:10.1002/bies.200900192) - DOI - PubMed
-
- McFall-Ngai M, et al. 2013. Animals in a bacterial world, a new imperative for the life sciences. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 3229–3236. (doi:10.1073/pnas.1218525110) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bright M, Bulgheresi S. 2010. A complex journey: transmission of microbial symbionts. Nat. Rev. Micro. 8, 218–230. (doi:10.1038/nrmicro2262) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dillon RJ, Dillon VM. 2004. The gut bacteria of insects: nonpathogenic interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 49, 71–92. (doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.49.061802.123416) - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
