Individual-based modelling and control of bovine brucellosis
- PMID: 29892455
- PMCID: PMC5990817
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.180200
Individual-based modelling and control of bovine brucellosis
Abstract
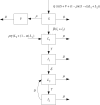
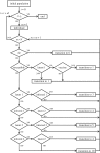
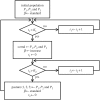
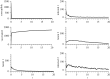
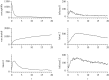
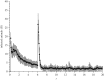
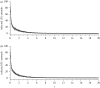
We present a theoretical approach to control bovine brucellosis. We have used individual-based modelling, which is a network-type alternative to compartmental models. Our model thus considers heterogeneous populations, and spatial aspects such as migration among herds and control actions described as pulse interventions are also easily implemented. We show that individual-based modelling reproduces the mean field behaviour of an equivalent compartmental model. Details of this process, as well as flowcharts, are provided to facilitate the reproduction of the presented results. We further investigate three numerical examples using real parameters of herds in the São Paulo state of Brazil, in scenarios which explore eradication, continuous and pulsed vaccination and meta-population effects. The obtained results are in good agreement with the expected behaviour of this disease, which ultimately showcases the effectiveness of our theory.
Keywords: bovine brucellosis; individual-based model; mathematical epidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Borba MR. 2013. Prevalence and risk-mapping of bovine brucellosis in Maranhão State, Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 110, 169–176. (doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2012.11.013) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Musallam II, Abo-Shehada M, Omar M, Guitian J. 2015. Cross-sectional study of brucellosis in Jordan: prevalence, risk factors and spatial distribution in small ruminants and cattle. Prev. Vet. Med. 118, 387–396. (doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2014.12.020) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Souza VAF, Ferreira Neto JS, Amaku M, Dias RA, Telles EO, Hildebrand Grisi-Filho JH, Heinemann MB, Ferreira F. 2016. Mathematical modeling of bovine brucellosis control using the RB51 vaccine. Semina: Ciênc. Agrár. 37, 3767–3775. (doi:10.5433/1679-0359.2016v37n5Supl2p3767) - DOI
-
- Inchaisri C, Prasomsri P, Boonserm T, Hogeveen H, Ajariyakajorn K. 2016. A stochastic simulation model for brucellosis eradication in goat flocks in an area with high flock prevalence but low animal prevalence. Small Ruminant Res. 136, 227–237. (doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2016.02.005) - DOI
-
- Hou Q, Zhang F. 2016. Global dynamics of a general brucellosis model with discrete delay. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 6, 227–241. (doi:10.11948/2016019) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
