Recurrence of Critical Limb Ischemia After Endovascular Intervention in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- PMID: 29892493
- PMCID: PMC5994148
- DOI: 10.1089/wound.2017.0778
Recurrence of Critical Limb Ischemia After Endovascular Intervention in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Abstract
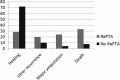
Objective: To establish the rate of clinical recurrence of critical limb ischemia (CLI) in diabetic patients with ischemic foot ulcers (DFUs) treated by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA). Approach: The study group was composed of 304 patients with ischemic DFUs treated by PTA. We evaluated the rate of clinical recurrence of CLI requiring a second PTA (repeated PTA [rePTA]), the factors related to CLI relapse, and the outcomes of rePTA patients. The follow-up was 12.5 ± 6.6 months. Results: Seventy-four of 304 patients (24.3%) needed rePTA. The mean time to rePTA was 3.5 ± 0.64 months. rePTA group in comparison with no rePTA group had lower rate of healing (28.5% vs. 71.9% p = 0.0001), higher rate of ulcer recurrence (20% vs. 10.3% p = 0.03), major amputation (24.3% vs. 4.3% p = 0.0005), and death (33.3% vs. 7.9% p = 0.002). Glycated hemoglobin, type A1C (HbA1c; 2.2 [1.9-2.7] p = 0.02) and dialysis (1.5 [1.4-3.6] p = 0.006) were independently associated to clinical recurrence of CLI after PTA. Innovation: To identify the outcomes of patients with clinical recurrence of CLI and the clinical factors involved to reduce the rate of restenosis after endovascular treatment and improve the rate of limb salvage. Conclusions: Clinical recurrence of CLI is associated with a high rate of nonhealing ulcer recurrence, major amputation, and death. Dialysis and impaired glycemic control were independent predictors of CLI relapse after endovascular treatment.
Keywords: critical limb ischemia; diabetes; diabetic foot ulcers; limb salvage; revascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist. The content of this article was expressly written by the authors listed. No ghostwriters were used to write this article.
Figures
References
-
- Jude B, Eleftheriadou I, Tentolouris N. Peripheral arterial disease in diabetes. Diabet Med 2010;27:4–14 - PubMed
-
- Faglia E, Caravaggi C, Marchetti R, et al. . Screening for peripheral arterial disease by means of the ankle-brachial index in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med 2005;22:1310–1314 - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist J, Elgzyri T, Larsson J, Londahl M, Nyberg P, Thorne J. Factors related to outcome of neuroischemic/ischemic foot ulcer in diabetic patients. J Vasc Surg 2011;53:1582–1588 - PubMed
-
- McNeely MJ, Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, et al. . The independent contributions of diabetic neuropathy and vasculopathy in foot ulceration. How great are the risks? Diabetes Care 1995;18:216–219 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous