A study on the prevalence of the anconeus epitrochlearis muscle by magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 29892591
- PMCID: PMC5993924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rboe.2018.03.015
A study on the prevalence of the anconeus epitrochlearis muscle by magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
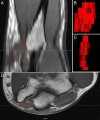
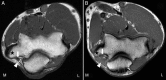
Objective: To analyze magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the elbow area to quantify the presence of the anconeus epitrochlearis muscle.
Methods: A total of 232 exams were analyzed; 218 were included, of which 141 were of men and 77, women.
Results: Presence of the muscle was observed in 29 cases (13.3%), demonstrating that the presence of this muscle on images does not have a statistical correlation with the gender or age of the individual.
Conclusion: The prevalence of the anconeus epitrochlearis muscle is variable, without a pattern of normality.
Objetivo: Analisar imagens de ressonância magnética da região do cotovelo para quantificar a presença o músculo ancôneo epitroclear.
Métodos: Foram analisados 232 exames, foram incluídos 218, dos quais 141 eram homens e 77 mulheres.
Resultados: Observou-se a presença do músculo em 29 casos (13,3%), a presença desse músculo em imagens não apresentou correlação estatística com o gênero ou com a idade do indivíduo.
Conclusão: A prevalência do músculo ancôneo epitroclear é variável, sem a presença de um padrão de normalidade.
Keywords: Anatomical variation; Musculoskeletal system; Upper limb.
Figures
References
-
- Gessini L., Jandolo B., Pietrangeli A., Occhipinti E. Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow by persistent epitrochleoanconeus muscle. J Neurosurg. 1981;55(5):830–831. - PubMed
-
- Dekelver I., Van Glabbeek F., Dijs H., Stassijns G. Bilateral ulnar nerve entrapment by the M. anconeus epitrochlearis. A case report and literature review. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(7):1139–1142. - PubMed
-
- Testut L. Masson; Paris: 1884. Les anomalies musculaires chez l’homme. Expliquées par l’anatomie comparée. Leur importance en anthropologie.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
