Molecular signature of Epstein-Barr virus infection in MS brain lesions
- PMID: 29892607
- PMCID: PMC5994704
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000466
Molecular signature of Epstein-Barr virus infection in MS brain lesions
Abstract
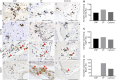
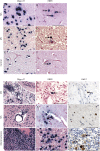
Objective: We sought to confirm the presence and frequency of B cells and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (latent and lytic phase) antigens in archived MS and non-MS brain tissue by immunohistochemistry.
Methods: We quantified the type and location of B-cell subsets within active and chronic MS brain lesions in relation to viral antigen expression. The presence of EBV-infected cells was further confirmed by in situ hybridization to detect the EBV RNA transcript, EBV-encoded RNA-1 (EBER-1).
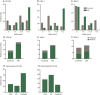
Results: We report the presence of EBV latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) in 93% of MS and 78% of control brains, with a greater percentage of MS brains containing CD138+ plasma cells and LMP-1-rich populations. Notably, 78% of chronic MS lesions and 33.3% of non-MS brains contained parenchymal CD138+ plasma cells. EBV early lytic protein, EBV immediate-early lytic gene (BZLF1), was also observed in 46% of MS, primarily in association with chronic lesions and 44% of non-MS brain tissue. Furthermore, 85% of MS brains revealed frequent EBER-positive cells, whereas non-MS brains seldom contained EBER-positive cells. EBV infection was detectable, by immunohistochemistry and by in situ hybridization, in both MS and non-MS brains, although latent virus was more prevalent in MS brains, while lytic virus was restricted to chronic MS lesions.
Conclusions: Together, our observations suggest an uncharacterized link between the EBV virus life cycle and MS pathogenesis.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
