The wound-healing effects of a next-generation anti-biofilm silver Hydrofiber wound dressing on deep partial-thickness wounds using a porcine model
- PMID: 29893025
- PMCID: PMC7949536
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12935
The wound-healing effects of a next-generation anti-biofilm silver Hydrofiber wound dressing on deep partial-thickness wounds using a porcine model
Abstract
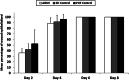
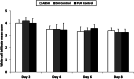
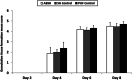
Topical antimicrobials are widely used to control wound bioburden and facilitate wound healing; however, the fine balance between antimicrobial efficacy and non-toxicity must be achieved. This study evaluated whether an anti-biofilm silver-containing wound dressing interfered with the normal healing process in non-contaminated deep partial thickness wounds. In an in-vivo porcine wound model using 2 pigs, 96 wounds were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 dressing groups: anti-biofilm silver Hydrofiber dressing (test), silver Hydrofiber dressing (control), or polyurethane film dressing (control). Wounds were investigated for 8 days, and wound biopsies (n = 4) were taken from each dressing group, per animal, on days 2, 4, 6, and 8 after wounding and evaluated using light microscopy. No statistically significant differences were observed in the rate of reepithelialisation, white blood cell infiltration, angiogenesis, or granulation tissue formation following application of the anti-biofilm silver Hydrofiber dressing versus the 2 control dressings. Overall, epithelial thickness was similar between groups. Some differences in infiltration of specific cell types were observed between groups. There were no signs of tissue necrosis, fibrosis, or fatty infiltration in any group. An anti-biofilm silver Hydrofiber wound dressing did not cause any notable interference with normal healing processes.
Keywords: anti-biofilm dressings; healing; partial thickness wounds; porcine model; silver.
© 2018 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preclinical evaluation of a novel silver gelling fiber dressing on Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a porcine wound infection model.Wound Repair Regen. 2019 Jul;27(4):360-365. doi: 10.1111/wrr.12718. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Wound Repair Regen. 2019. PMID: 30920083
-
Clinical and in vitro performance of an antibiofilm Hydrofiber wound dressing.J Wound Care. 2018 Sep 2;27(9):584-592. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2018.27.9.584. J Wound Care. 2018. PMID: 30204577
-
The effect of negative pressure wound therapy with antibacterial dressings or antiseptics on an in vitro wound model.J Wound Care. 2017 May 2;26(5):236-242. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2017.26.5.236. J Wound Care. 2017. PMID: 28475440
-
Silver-containing foam dressings with Safetac: a review of the scientific and clinical data.J Wound Care. 2017 Jun 1;26(Sup6a):S1-S32. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2017.26.Sup6a.S1. J Wound Care. 2017. PMID: 28594320 Review.
-
Effect of silver-containing hydrofiber dressing on burn wound healing: A meta-analysis and systematic review.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 May;22(5):1685-1691. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15639. Epub 2023 Jan 22. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36683314
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial effectiveness of wound matrices containing native extracellular matrix with polyhexamethylene biguanide.Int Wound J. 2022 Jan;19(1):86-99. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13600. Epub 2021 May 6. Int Wound J. 2022. PMID: 33955663 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane in the Treatment of Diabetic Wounds.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 21;14(1):6. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010006. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Chronic Wound Healing through Electrical Stimulation and Adipose-Derived Stem Cells.Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Apr;14(10):e2403777. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202403777. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025. PMID: 40025921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silver Sulfadiazine Eradicates Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms in Patients with Infected Diabetic Foot Ulcers.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 25;9(12):3807. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123807. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33255545 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical impact of an anti-biofilm Hydrofiber dressing in hard-to-heal wounds previously managed with traditional antimicrobial products and systemic antibiotics.Burns Trauma. 2020 Mar 4;8:tkaa004. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkaa004. eCollection 2020. Burns Trauma. 2020. PMID: 32341917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leaper D, Assadian O, Edmiston CE. Approach to chronic wound infections. Br J Dermatol. 2015;173(2):351‐358. - PubMed
-
- Wolcott R, Sanford N, Gabrilska R, Oates JL, Wilkinson JE, Rumbaugh KP. Microbiota is a primary cause of pathogenesis of chronic wounds. J Wound Care. 2016;25(suppl 10):S33‐S43. - PubMed
-
- Metcalf D, Bowler P, Parsons D. Wound biofilm and therapeutic strategies. In: Dhanasekaran D, Thajuddin N, eds. Microbial Biofilms – Importance and Applications. Tiruchirappalli, India: IN TECH; 2016:271‐298.
-
- Bowler PG, Parsons D. Combatting wound biofilm and recalcitrance with a novel anti‐biofilm Hydrofiber® wound dressing. Wound Med. 2016;14:6‐11.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

