Biocomputing for Portable, Resettable, and Quantitative Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Making the Glucose Meter a Logic-Gate Responsive Device for Measuring Many Clinically Relevant Targets
- PMID: 29893502
- PMCID: PMC6261302
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201804292
Biocomputing for Portable, Resettable, and Quantitative Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Making the Glucose Meter a Logic-Gate Responsive Device for Measuring Many Clinically Relevant Targets
Abstract
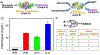
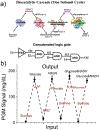
It is recognized that biocomputing can provide intelligent solutions to complex biosensing projects. However, it remains challenging to transform biomolecular logic gates into convenient, portable, resettable and quantitative sensing systems for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics in a low-resource setting. To overcome these limitations, the first design of biocomputing on personal glucose meters (PGMs) is reported, which utilizes glucose and the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide as signal outputs, DNAzymes and protein enzymes as building blocks, and demonstrates a general platform for installing logic-gate responses (YES, NOT, INHIBIT, NOR, NAND, and OR) to a variety of biological species, such as cations (Na+ ), anions (citrate), organic metabolites (adenosine diphosphate and adenosine triphosphate) and enzymes (pyruvate kinase, alkaline phosphatase, and alcohol dehydrogenases). A concatenated logical gate platform that is resettable is also demonstrated. The system is highly modular and can be generally applied to POC diagnostics of many diseases, such as hyponatremia, hypernatremia, and hemolytic anemia. In addition to broadening the clinical applications of the PGM, the method reported opens a new avenue in biomolecular logic gates for the development of intelligent POC devices for on-site applications.
Keywords: DNA; biosensing; enzyme cascades; glucose meter; point-of-care testing.
© 2018 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- a) Zhan W, Crooks RM, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9934–9935; - PubMed
- b) Zhou M, Du Y, Chen CG, Li BL, Wen D, Dong SJ, Wang EK, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2172–2174; - PubMed
- c) Chang B-Y; Crooks JA; Chow K-F; Mavré F; Crooks RM, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15404–15409; - PubMed
- d) Pei H, Liang L, Yao GB, Li J, Huang Q, Fan CH, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9020–9024; - PubMed
- e) Katz E, Minko S, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3493–3500; - PubMed
- f) He KY, Li Y, Xiang BB, Zhao P, Hu YF, Huang Y, Li W, Nie Z, Yao SZ, Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 3556–3564; - PMC - PubMed
- g) Li DD, Cheng W, Li YJ, Xu YJ, Li XM, Yin YB, Ju HX, Ding SJ, Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7500–7506; - PubMed
- h) Molinnus D, Poghossian A, Keusgen M, Katz E, Schoning MJ, Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1840–1849; - PMC - PubMed
- i) Li Y, Sun SJ, Fan L, Hu SF, Huang Y, Zhang K, Nie Z, Yao SZ, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14888–14892; - PubMed
- j) Liang JY, Yu X, Yang TG, Li ML, Shen L, Jin Y, Liu HY, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22472–22481; - PubMed
- k) Qu XM, Zhu D, Yao GB, Su S, Chao J, Liu HJ, Zuo XL, Wang LH, Shi JY, Wang LH, Huang W, Pei H, Fan CH, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1855–1858; - PubMed
- l) Li J, Green AA, Yan H, Fan CH, Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 1056–1067; - PMC - PubMed
- m) Peng HY, Newbigging AM, Wang ZX, Tao J, Deng WC, Le XC, Zhang HQ, Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 190–207. - PubMed
-
- a) Lake A, Shang S, Kolpashchikov DM, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4459–4462; - PubMed
- b) Liu Y, Offenhausser A, Mayer D, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 2595–2598; - PubMed
- c) Benenson Y, Nat. Nanotech. 2011, 6, 465–467; - PubMed
- d) de Silva AP, Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 750–766; - PubMed
- e) Bel-Enguix G, Jiménez-López MD, Natural Computing 2012, 11, 131–139;
- f) Prokup A, Hemphill J, Deiters A, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3810–3815; - PubMed
- g) Gao JT, Liu YQ, Lin XD, Deng JK, Yin JJ, Wang S, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7 14014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Bi S, Ji B, Zhang ZP, Zhu JJ, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1858–1863;
- b) Zhang M, Ye BC, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3647–3649; - PubMed
- c) Guo YH, Wu J, Ju HX, Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4318–4323; - PMC - PubMed
- d) Wang WJ, Huang S, Li JJ, Rui K, Bi S, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 174–180; - PMC - PubMed
- e) Tang YD, Lu BY, Zhu ZT, Li BL, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 760–769. - PMC - PubMed
-
- a) Xianyu YL, Wang Z, Sun JS, Wang XF, Jiang XY, Small 2014, 10, 4833–4838; - PubMed
- b) Wu CT, Fan DQ, Zhou CY, Liu YQ, Wang EK, Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2899–2903; - PubMed
- c) Chen JH, Zhou SG, Wen JL, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 446–450; - PubMed
- d) Huang YY, Pu F, Ren JS, Qu XG, Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 9156–9161. - PubMed
-
- a) Tang LH, Wang Y, Li JH, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6954–6980; - PubMed
- b) Ge L, Wang WX, Sun XM, Hou T, Li F, Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9691–9698; - PubMed
- c) Zhai QF, Fan DQ, Zhang XW, Li J, Wang EK, Npg Asia Mater. 2017, 9;
- d) Du Y, Han X, Wang CX, Li YH, Li BL, Duan HW, ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 54–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

