The ADRP domain from a virulent strain of infectious bronchitis virus is not sufficient to confer a pathogenic phenotype to the attenuated Beaudette strain
- PMID: 29893665
- PMCID: PMC6171709
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001098
The ADRP domain from a virulent strain of infectious bronchitis virus is not sufficient to confer a pathogenic phenotype to the attenuated Beaudette strain
Abstract
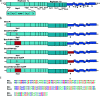
The replicase gene of the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) encodes 15 non-structural proteins (nsps). Nsp 3 is a multi-functional protein containing a conserved ADP-ribose-1″-phosphatase (ADRP) domain. The crystal structures of the domain from two strains of IBV, M41 (virulent) and Beaudette (avirulent), identified a key difference; M41 contains a conserved triple-glycine motif, whilst Beaudette contains a glycine-to-serine mutation that is predicted to abolish ADRP activity. Although ADRP activity has not been formally demonstrated for IBV nsp 3, Beaudette fails to bind ADP-ribose. The role of ADRP in virulence was investigated by generating rIBVs, based on Beaudette, containing either a restored triple-glycine motif or the complete M41 ADRP domain. Replication in vitro was unaffected by the ADRP modifications and the in vivo phenotype of the rIBVs was found to be apathogenic, indicating that restoration of the triple-glycine motif is not sufficient to restore virulence to the apathogenic Beaudette strain.
Keywords: ADRP; coronavirus; infectious bronchitis virus; macrodomain; nsp3; pathogenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Koonin EV, Lai MM. Putative papain-related thiol proteases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Identification of rubi- and aphthovirus proteases and delineation of a novel conserved domain associated with proteases of rubi-, alpha- and coronaviruses. FEBS Lett. 1991;288:201–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81034-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

