Ulk2 controls cortical excitatory-inhibitory balance via autophagic regulation of p62 and GABAA receptor trafficking in pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 29893844
- PMCID: PMC6121199
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy219
Ulk2 controls cortical excitatory-inhibitory balance via autophagic regulation of p62 and GABAA receptor trafficking in pyramidal neurons
Abstract
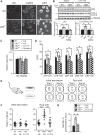
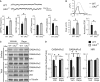
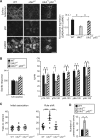
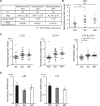
Autophagy plays an essential role in intracellular degradation and maintenance of cellular homeostasis in all cells, including neurons. Although a recent study reported a copy number variation of Ulk2, a gene essential for initiating autophagy, associated with a case of schizophrenia (SZ), it remains to be studied whether Ulk2 dysfunction could underlie the pathophysiology of the disease. Here we show that Ulk2 heterozygous (Ulk2+/-) mice have upregulated expression of sequestosome-1/p62, an autophagy-associated stress response protein, predominantly in pyramidal neurons of the prefrontal cortex (PFC), and exhibit behavioral deficits associated with the PFC functions, including attenuated sensorimotor gating and impaired cognition. Ulk2+/- neurons showed imbalanced excitatory-inhibitory neurotransmission, due in part to selective down-modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)A receptor surface expression in pyramidal neurons. Genetically reducing p62 gene dosage or suppressing p62 protein levels with an autophagy-inducing agent restored the GABAA receptor surface expression and rescued the behavioral deficits in Ulk2+/- mice. Moreover, expressing a short peptide that specifically interferes with the interaction of p62 and GABAA receptor-associated protein, a protein that regulates endocytic trafficking of GABAA receptors, also restored the GABAA receptor surface expression and rescued the behavioral deficits in Ulk2+/- mice. Thus, the current study reveals a novel mechanism linking deregulated autophagy to functional disturbances of the nervous system relevant to SZ, through regulation of GABAA receptor surface presentation in pyramidal neurons.
Figures

References
-
- Mizushima N., Komatsu M. (2011) Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell, 147, 728–741. - PubMed
-
- Hara T., Nakamura K., Matsui M., Yamamoto A., Nakahara Y., Suzuki-Migishima R., Yokoyama M., Mishima K., Saito I., Okano H., Mizushima N. (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature, 441, 885–889. - PubMed
-
- Komatsu M., Waguri S., Chiba T., Murata S., Iwata J., Tanida I., Ueno T., Koike M., Uchiyama Y., Kominami E., Tanaka K. (2006) Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature, 441, 880–884. - PubMed
-
- Komatsu M., Wang Q.J., Holstein G.R., Friedrich V.L. Jr, Iwata J., Kominami E., Chait B.T., Tanaka K., Yue Z. (2007) Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 104, 14489–14494. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

