Ongoing clinical trials and treatment options for patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 29893938
- PMCID: PMC6434373
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/key151
Ongoing clinical trials and treatment options for patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease
Abstract
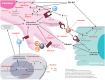
SSc is a rare CTD that affects multiple organ systems, resulting in substantial morbidity and mortality. Evidence of interstitial lung disease (ILD) is seen in ∼80% of patients with SSc. Currently there is no approved disease-modifying treatment for ILD and few effective treatment options are available. CYC is included in treatment guidelines, but it has limited efficacy and is associated with toxicity. MMF is becoming the most commonly used medication in clinical practice in North America and the UK, but its use is not universal. Newer agents targeting the pathogenic mechanisms underlying SSc-ILD, including fibrotic and inflammatory pathways, lymphocytes, cell-cell and cell-extracellular membrane interactions, hold promise for better treatment outcomes, including improved lung function, patient-related outcomes and quality of life. Here we review ongoing trials of established and novel agents that are currently recruiting patients with SSc-ILD.
Keywords: abituzumab; bortezomib; dabigatran; interstitial lung disease; nintedanib; pirfenidone; pulmonary fibrosis; study design; systemic sclerosis.
© The Author(s) 2018. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures
References
-
- Denton CP, Khanna D.. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017;390:1685–99. - PubMed
-
- Hinchcliff M, Varga J.. Systemic sclerosis/scleroderma: a treatable multisystem disease. Am Fam Physician 2008;78:961–8. - PubMed
-
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M. et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1809–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical