Convex mixture regression for quantitative risk assessment
- PMID: 29894557
- PMCID: PMC6650640
- DOI: 10.1111/biom.12917
Convex mixture regression for quantitative risk assessment
Abstract
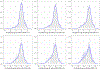
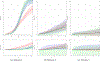
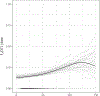
There is wide interest in studying how the distribution of a continuous response changes with a predictor. We are motivated by environmental applications in which the predictor is the dose of an exposure and the response is a health outcome. A main focus in these studies is inference on dose levels associated with a given increase in risk relative to a baseline. In addressing this goal, popular methods either dichotomize the continuous response or focus on modeling changes with the dose in the expectation of the outcome. Such choices may lead to information loss and provide inaccurate inference on dose-response relationships. We instead propose a Bayesian convex mixture regression model that allows the entire distribution of the health outcome to be unknown and changing with the dose. To balance flexibility and parsimony, we rely on a mixture model for the density at the extreme doses, and express the conditional density at each intermediate dose via a convex combination of these extremal densities. This representation generalizes classical dose-response models for quantitative outcomes, and provides a more parsimonious, but still powerful, formulation compared to nonparametric methods, thereby improving interpretability and efficiency in inference on risk functions. A Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm for posterior inference is developed, and the benefits of our methods are outlined in simulations, along with a study on the impact of dde exposure on gestational age.
Keywords: Additional risk; Benchmark dose; Conditional density estimation; Convex density regression; Dose-response; Nonparametric density regression.
© 2018, The International Biometric Society.
Figures
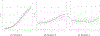
References
-
- Calabrese EJ and Baldwin LA (2001). U-shaped dose-responses in biology, toxicology, and public health. Annual Review of Public Health 22, 15–33. - PubMed
-
- Crump KS (1995). Calculation of benchmark doses from continuous data. Risk Analysis 15, 79–89.
-
- De Iorio M, Müller P, Rosner GL, and MacEachern SN (2004). An ANOVA model for dependent random measures. Journal of the American Statistical Association 99, 205–215.
-
- Fronczyk K and Kottas A (2014). A Bayesian nonparametric modeling framework for developmental toxicity studies. Journal of the American Statistical Association 109, 873–888.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

