Liver Cancer Initiation Requires p53 Inhibition by CD44-Enhanced Growth Factor Signaling
- PMID: 29894692
- PMCID: PMC6005359
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.05.003
Liver Cancer Initiation Requires p53 Inhibition by CD44-Enhanced Growth Factor Signaling
Abstract
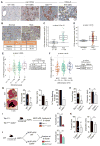
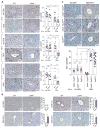
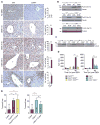
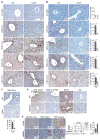
How fully differentiated cells that experience carcinogenic insults become proliferative cancer progenitors that acquire multiple initiating mutations is not clear. This question is of particular relevance to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which arises from differentiated hepatocytes. Here we show that one solution to this problem is provided by CD44, a hyaluronic acid receptor whose expression is rapidly induced in carcinogen-exposed hepatocytes in a STAT3-dependent manner. Once expressed, CD44 potentiates AKT activation to induce the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Mdm2, which terminates the p53 genomic surveillance response. This allows DNA-damaged hepatocytes to escape p53-induced death and senescence and respond to proliferative signals that promote fixation of mutations and their transmission to daughter cells that go on to become HCC progenitors.
Keywords: CD44; DNA damage response; EGFR; HCC; MDM2 nuclear translocation; cancer initiation; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver cancer; p53; p53 termination.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

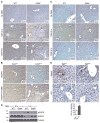
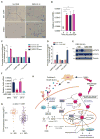
Comment in
-
MDM2-TP53 Crossregulation: An Underestimated Target to Promote Loss of TP53 Function and Cell Survival.Trends Cancer. 2018 Sep;4(9):602-605. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Trends Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30149877
References
-
- Bergmann J, Muller M, Baumann N, Reichert M, Heneweer C, Bolik J, Lucke K, Gruber S, Carambia A, Boretius S, et al. IL-6 trans-signaling is essential for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology. 2017;65:89–103. - PubMed
-
- Bettermann K, Vucur M, Haybaeck J, Koppe C, Janssen J, Heymann F, Weber A, Weiskirchen R, Liedtke C, Gassler N, et al. TAK1 suppresses a NEMO-dependent but NF-kappaB-independent pathway to liver cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:481–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

