Lipidation of polyethylenimine-based polyplex increases serum stability of bioengineered RNAi agents and offers more consistent tumoral gene knockdown in vivo
- PMID: 29894758
- PMCID: PMC6388695
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.06.026
Lipidation of polyethylenimine-based polyplex increases serum stability of bioengineered RNAi agents and offers more consistent tumoral gene knockdown in vivo
Abstract
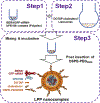
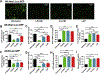
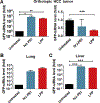
Recently we have established a novel approach to produce bioengineered noncoding RNA agents (BERAs) in living cells that carry target RNAi molecules (e.g., siRNA and miRNA) and thus act as "prodrugs". Using GFP-siRNA-loaded BERA (BERA/GFP-siRNA) as a model molecule, this study was to define the in vitro and in vivo knockdown efficiency of BERAs delivered by liposome-polyethylenimine nanocomplex (lipopolyplex or LPP). Compared to in vivo-jetPEI® (IVJ-PEI) and polyplex formulations, LPP offered greater protection of BERA/GFP-siRNA against degradation by serum RNases. Particle sizes and zeta potentials of LPP nanocomplex remained stable over 28 days when stored at 4 °C. Furthermore, comparable levels of BERA/GFP-siRNA were delivered by LPP and IVJ-PEI to luciferase/GFP-expressing human SK-Hep1-Luc-GFP or A549-Luc-GFP cells, which were selectively processed into target GFP-siRNA and subsequently knocked down GFP mRNA and protein levels. In addition, LPP-carried BERA/GFP-siRNA was successfully delivered into xenograft tumors and offered more consistent knockdown of tumoral GFP mRNA level in an orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) SK-Hep1-Luc-GFP xenograft mouse model, while IVJ-PEI formulation showed larger variation. These findings demonstrated that lipidation of polyplexes improved serum stability of biologic RNAi molecules, which was efficiently delivered to orthotopic HCC tissues to knock down target gene expression.
Keywords: Bioengineering; Cancer; Lipopolyplex; Mouse model; Orthotopic HCC; RNA delivery; siRNA.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

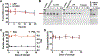
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

