Endoplasmic reticulum stress in ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 29895209
- PMCID: PMC6333465
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2018.1489142
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury
Abstract
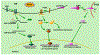
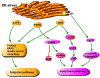
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a medical condition characterized by kidney damage with a rapid decline of renal function, which is associated with high mortality and morbidity. Recent research has further established an intimate relationship between AKI and chronic kidney disease. Perturbations of kidney cells in AKI result in the accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), leading to unfolded protein response (UPR) or ER stress. In this review, we analyze the role and regulation of ER stress in AKI triggered by renal ischemia-reperfusion and cisplatin nephrotoxicity. The balance between the two major components of UPR, the adaptive pathway and the apoptotic pathway, plays a critical role in determining the cell fate in ER stress. The adaptive pathway is evoked to attenuate translation, induce chaperones, maintain protein homeostasis and promote cell survival. Prolonged ER stress activates the apoptotic pathway, resulting in the elimination of dysfunctional cells. Therefore, regulating ER stress in kidney cells may provide a therapeutic target in AKI. KEY MESSAGES Perturbations of kidney cells in acute kidney injury result in the accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in ER, leading to unfolded protein response (UPR) or ER stress. The balance between the adaptive pathway and the apoptotic pathway of UPR plays a critical role in determining the cell fate in ER stress. Modulation of ER stress in kidney cells may provide a therapeutic strategy for acute kidney injury.
Keywords: Endoplasmic reticulum stress; acute kidney injury; apoptosis; autophagy; cisplatin; ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and its effects on renal tubular cells apoptosis in ischemic acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2016 Jun;38(5):831-7. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2016.1160724. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Ren Fail. 2016. PMID: 27001462 Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress is activated in post-ischemic kidneys to promote chronic kidney disease.EBioMedicine. 2018 Nov;37:269-280. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.10.006. Epub 2018 Oct 9. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30314894 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Autophagy Provides Cytoprotection from Chemical Hypoxia and Oxidant Injury and Ameliorates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 7;10(10):e0140025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140025. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26444017 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated acute kidney injury in juvenile rats and the protective role of mesencephalic astrocyte-derived neurotrophic factor.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2025 May 2;77(5):609-620. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgae134. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39437337
-
A review on endoplasmic reticulum-dependent anti-breast cancer activity of herbal drugs: possible challenges and opportunities.J Drug Target. 2025 Feb;33(2):206-231. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2024.2417189. Epub 2024 Oct 24. J Drug Target. 2025. PMID: 39404107 Review.
Cited by
-
Unexpected Enhancement of Cytotoxicity of Cisplatin in a Rat Kidney Proximal Tubular Cell Line Overexpressing Mitochondrial Glutathione Transport Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 11;23(4):1993. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041993. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216119 Free PMC article.
-
Diallyl Trisulfide Attenuates Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced ER Stress and Kidney Dysfunction in Aged Female Mice.Cells. 2025 Mar 12;14(6):420. doi: 10.3390/cells14060420. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40136669 Free PMC article.
-
Isoliquiritigenin Pretreatment Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Hormesis and Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Damage in LLC-PK1 Cells.Molecules. 2020 Sep 27;25(19):4442. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194442. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32992605 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Pathological Mechanisms, Pharmacological Interventions, and Genetic Mitigations.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 29;13(7):1572. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071572. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene Expression of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress During Septic Shock.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Nov 1;6:240. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00240. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31737637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inagi R, Ishimoto Y, Nangaku M. Proteostasis in endoplasmic reticulum--new mechanisms in kidney disease. Nature reviews Nephrology. 2014;10(7):369–78. - PubMed
-
- Walter P, Ron D. The unfolded protein response: from stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science. 2011;334(6059):1081–6. - PubMed
-
- Sommer T, Jarosch E. BiP binding keeps ATF6 at bay. Developmental cell. 2002;3(1):1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
