Printed 5-V organic operational amplifiers for various signal processing
- PMID: 29895859
- PMCID: PMC5997680
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27205-7
Printed 5-V organic operational amplifiers for various signal processing
Abstract
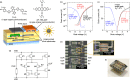
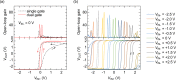
The important concept of printable functional materials is about to cause a paradigm shift that we will be able to fabricate electronic devices by printing methods in air at room temperature. One of the promising applications of the printed electronics is a disposable electronic patch sensing system which can monitor the health conditions without any restraint. Operational amplifiers (OPAs) are an essential component for such sensing system, since an OPA enables a wide variety of signal processing. Here we demonstrate printed OPAs based on complementary organic semiconductor technology. They can be operated with a standard safe power source of 5 V with a minimal power consumption of 150 nW, and used as amplifiers, a variety of mathematical operators, signal converters, and oscillators. The printed micropower organic OPAs with the low voltage operation and the high versatility will open up the disposable electronic patch sensing system in near future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Teichler A, et al. Inkjet printing of organic electronics – comparison of deposition techniques and state-of-the-art developments. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2013;1:1910. doi: 10.1039/c2tc00255h. - DOI
-
- Zhou L, et al. All-organic active matrix flexible display. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006;88:083502. doi: 10.1063/1.2178213. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

