Multimodality cellular and molecular imaging of concomitant tumour enhancement in a syngeneic mouse model of breast cancer metastasis
- PMID: 29895974
- PMCID: PMC5997674
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27208-4
Multimodality cellular and molecular imaging of concomitant tumour enhancement in a syngeneic mouse model of breast cancer metastasis
Abstract
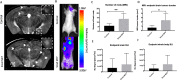
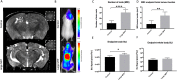
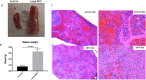
The mechanisms that influence metastatic growth rates are poorly understood. One mechanism of interest known as concomitant tumour resistance (CTR) can be defined as the inhibition of metastasis by existing tumour mass. Conversely, the presence of a primary tumour has also been shown to increase metastatic outgrowth, termed concomitant tumour enhancement (CTE). The majority of studies evaluating CTR/CTE in preclinical models have relied on endpoint histological evaluation of tumour burden. The goal of this research was to use conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), cellular MRI, and bioluminescence imaging to study the impact of a primary tumour on the development of brain metastases in a syngeneic mouse model. Here, we report that the presence of a 4T1 primary tumour significantly enhances total brain tumour burden in Balb/C mice. Using in vivo BLI/MRI we could determine this was not related to differences in initial arrest or clearance of viable cells in the brain, which suggests that the presence of a primary tumour can increase the proliferative growth of brain metastases in this model. The continued application of our longitudinal cellular and molecular imaging tools will yield a better understanding of the mechanism(s) by which this physiological inhibition (CTR) and/or enhancement (CTE) occurs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. Cancer Statistics. 2014;64(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G, Yu Y. Breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2012;9(5):311–320. - PubMed
-
- Chiarella, P., Bruzzo, J., Meiss, R. P., Ruggiero, R. A. Concomitant tumor resistance. Cancer Lett. 28, 324(2): 133–41 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Prehn RT. The inhibition of tumor growth by tumor mass. Cancer Res. 1991;51:2–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

