An essential role for Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mediating hypertensive heart disease
- PMID: 29895976
- PMCID: PMC5997634
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27064-2
An essential role for Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mediating hypertensive heart disease
Abstract
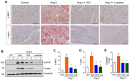
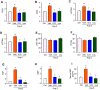
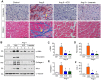
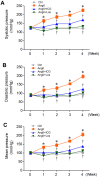
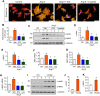
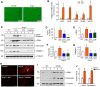
Activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is associated with hypertension and heart disease. However, how RAS activation causes cardiac lesions remains elusive. Here we report the involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in this process. In rats with chronic infusion of angiotensin II (Ang II), eight Wnt ligands were induced and β-catenin activated in both cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. Blockade of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by small molecule inhibitor ICG-001 restrained Ang II-induced cardiac hypertrophy by normalizing heart size and inhibiting hypertrophic marker genes. ICG-001 also attenuated myocardial fibrosis and inhibited α-smooth muscle actin, fibronectin and collagen I expression. These changes were accompanied by a reduced expression of atrial natriuretic peptide and B-type natriuretic peptide. Interestingly, ICG-001 also lowered blood pressure induced by Ang II. In vitro, Ang II induced multiple Wnt ligands and activated β-catenin in rat primary cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts. ICG-001 inhibited myocyte hypertrophy and Snail1, c-Myc and atrial natriuretic peptide expression, and abolished the fibrogenic effect of Ang II in cardiac fibroblasts. Finally, recombinant Wnt3a was sufficient to induce cardiomyocyte injury and fibroblast activation in vitro. Taken together, these results illustrate an essential role for Wnt/β-catenin in mediating hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis. Therefore, blockade of this pathway may be a novel strategy for ameliorating hypertensive heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

