Associations of MAP2K3 Gene Variants With Superior Memory in SuperAgers
- PMID: 29896098
- PMCID: PMC5987172
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00155
Associations of MAP2K3 Gene Variants With Superior Memory in SuperAgers
Abstract
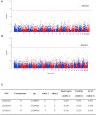
Introduction: SuperAgers are adults age 80+ with episodic memory performance that is at least as good as that of average middle-aged adults. Understanding the biological determinants of SuperAging may have relevance to preventing age-related cognitive decline and dementia. This study aimed to identify associations between genetic variations and the SuperAging phenotype using Whole Exome Sequencing (WES). Methods: Sequence Kernel Association Combined (SKAT-C) test was conducted at the gene level including both rare and common variants in 56 SuperAgers and 22 cognitively-average controls from the Alzheimer's disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). Results: The SuperAging phenotype was associated with variants in the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase 3 (MAP2K3) gene. Three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) contributed to the significance (rs2363221 [intron 1], rs2230435 [exon 5], rs736103 [intron 7]). Conclusions: MAP2K3 resides in a biological pathway linked to memory. It is in a signaling cascade associated with beta-amyloid mediated apoptosis and has enriched expression in microglia. This preliminary work suggests MAP2K3 may represent a novel therapeutic target for age-related memory decline and perhaps Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; Alzheimer’s dementia; Alzheimer’s disease (AD); aging; cognition; episodic memory; genetics; successful aging; whole exome sequencing.
Figures
References
-
- Bellenguez C., Charbonnier C., Grenier-Boley B., Quenez O., Le Guennec K., Nicolas G., et al. (2017). Contribution to Alzheimer’s disease risk of rare variants in TREM2, SORL1, and ABCA7 in 1779 cases and 1273 controls. Neurobiol. Aging 59, 220.e1–220.e9. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clayton D. (2015). snpStats: SnpMatrix and XSnpMatrix classes and methods. R package version 1.20.0.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

