Anti-neuroinflammatory Potential of Natural Products in Attenuation of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 29896105
- PMCID: PMC5986949
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00548
Anti-neuroinflammatory Potential of Natural Products in Attenuation of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
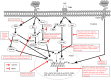
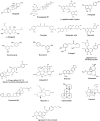
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic progressive neurodegenerative disorder associated with dementia and cognitive impairment most common in elderly population. Various pathophysiological mechanisms have been proposed by numerous researcher, although, exact mechanism is not yet elucidated. Several studies have been indicated that neuroinflammation associated with deposition of amyloid- beta (Aβ) in brain is a major hallmark toward the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. So, there is a need to unravel the link of inflammatory process in neurodegeneration. Increased microglial activation, expression of cytokines, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) participate in inflammatory process of AD. This review mainly concentrates on involvement of neuroinflammation and the molecular mechanisms adapted by various natural compounds, phytochemicals and herbal formulations in various signaling pathways involved in neuroprotection. Currently, pharmacologically active natural products, having anti-neuroinflammatory potential are being focused which makes them potential candidate to cure AD. A number of preclinical and clinical trials have been done on nutritional and botanical agents. Analysis of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective phytochemicals such as terpenoids, phenolic derivatives, alkaloids, glycosides, and steroidal saponins displays therapeutic potential toward amelioration and prevention of devastating neurodegeneration observed in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; herbal formulation; natural products; neuroinflammation; neuroprotection; phytochemicals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Potential of Different Natural Products for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 22;2022:6873874. doi: 10.1155/2022/6873874. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35910833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Steroid and Terpenoid-Derived Phytochemicals to Combat Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(22):2635-2647. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666210101152352. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33463452 Review.
-
Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer's Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Dec 19;10:427. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00427. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29311817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contribution of neuroinflammation to amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem. 2016 Feb;136(3):457-74. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13411. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26509334 Review.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Polyphenols by Inhibiting NF-κB to Halt Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(3):402-414. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666201118092422. Curr Pharm Des. 2021. PMID: 33213314 Review.
Cited by
-
An Aqueous Extract of Herbal Medicine ALWPs Enhances Cognitive Performance and Inhibits LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation via FAK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Sep 26;10:269. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00269. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30319390 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Natural Compounds and Target Enzymes in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2022 Jun 29;27(13):4175. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134175. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy, safety, and response predictors of Astragalus in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: A study protocol of an assessor-blind, statistician-blind open-label randomized controlled trial.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024 Jul 28;41:101339. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101339. eCollection 2024 Oct. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024. PMID: 39176240 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Activity and Neuroprotective Activity of Stilbenoids in Rat Primary Cortex Neurons via the PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway.Molecules. 2018 Sep 12;23(9):2328. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092328. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30213108 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Natural Products in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2023 Feb 3;28(3):1486. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031486. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal B. B., Harikumar K. B. (2009). Potential therapeutic effects of curcumin, the anti-inflammatory agent, against neurodegenerative, cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, autoimmune and neoplastic diseases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41, 40–59. 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.06.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

