Blood-Bourne MicroRNA Biomarker Evaluation in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder of Han Chinese Individuals: An Exploratory Study
- PMID: 29896131
- PMCID: PMC5987559
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00227
Blood-Bourne MicroRNA Biomarker Evaluation in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder of Han Chinese Individuals: An Exploratory Study
Abstract
Background: Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a highly genetic neurodevelopmental disorder, and its dysregulation of gene expression involves microRNAs (miRNAs). The purpose of this study was to identify potential miRNAs biomarkers and then use these biomarkers to establish a diagnostic panel for ADHD. Design and methods: RNA samples from white blood cells (WBCs) of five ADHD patients and five healthy controls were combined to create one pooled patient library and one control library. We identified 20 candidate miRNAs with the next-generation sequencing (NGS) technique (Illumina). Blood samples were then collected from a Training Set (68 patients and 54 controls) and a Testing Set (20 patients and 20 controls) to identify the expression profiles of these miRNAs with real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). We used receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and the area under the curve (AUC) to evaluate both the specificity and sensitivity of the probability score yielded by the support vector machine (SVM) model. Results: We identified 13 miRNAs as potential ADHD biomarkers. The ΔCt values of these miRNAs in the Training Set were integrated to create a biomarker model using the SVM algorithm, which demonstrated good validity in differentiating ADHD patients from control subjects (sensitivity: 86.8%, specificity: 88.9%, AUC: 0.94, p < 0.001). The results of the blind testing showed that 85% of the subjects in the Testing Set were correctly classified using the SVM model alignment (AUC: 0.91, p < 0.001). The discriminative validity is not influenced by patients' age or gender, indicating both the robustness and the reliability of the SVM classification model. Conclusion: As measured in peripheral blood, miRNA-based biomarkers can aid in the differentiation of ADHD in clinical settings. Additional studies are needed in the future to clarify the ADHD-associated gene functions and biological mechanisms modulated by miRNAs.
Keywords: ADHD; biomarker; diagnosis; epigenetic; miRNA.
Figures

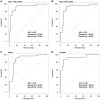
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs serve as prediction and treatment-response biomarkers of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and promote the differentiation of neuronal cells by repressing the apoptosis pathway.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 19;12(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01832-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35184133 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of miRNAs in serum of children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder shows significant alterations.J Psychiatr Res. 2019 Feb;109:185-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.12.013. Epub 2018 Dec 8. J Psychiatr Res. 2019. PMID: 30557705
-
MicroRNA profile as potential molecular signature for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children.Biomarkers. 2022 May;27(3):230-239. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2021.2024600. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Biomarkers. 2022. PMID: 34989306
-
Blood miRNA levels associated with ADHD traits in children across six European birth cohorts.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Sep 25;23(1):696. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05199-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37749515 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in serum miRNA-let-7 level in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder treated by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation or atomoxetine: An exploratory trial.Psychiatry Res. 2019 Apr;274:189-194. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.02.037. Epub 2019 Feb 17. Psychiatry Res. 2019. PMID: 30807970 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
MiRNA profiles in blood plasma from mother-child duos in human biobanks and the implication of sample quality: Circulating miRNAs as potential early markers of child health.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 2;15(4):e0231040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231040. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32240265 Free PMC article.
-
The Computational Analysis Conducted on miRNA Target Sites in Association with SNPs at 3'UTR of ADHD-implicated Genes.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(1):58-75. doi: 10.2174/1871524919666191014104843. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31660846 Free PMC article.
-
From Plants to Psycho-Neurology: Unravelling the Therapeutic Benefits of Bioactive Compounds in Brain Disorders.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;12(8):1603. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081603. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using artificial intelligence methods to study the effectiveness of exercise in patients with ADHD.Front Neurosci. 2024 Apr 23;18:1380886. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1380886. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38716252 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs serve as prediction and treatment-response biomarkers of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and promote the differentiation of neuronal cells by repressing the apoptosis pathway.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 19;12(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-01832-1. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35184133 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

