A Rapid and Specific Assay for the Detection of MERS-CoV
- PMID: 29896174
- PMCID: PMC5987675
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01101
A Rapid and Specific Assay for the Detection of MERS-CoV
Abstract
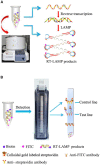
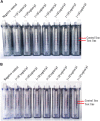
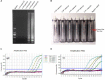
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a novel human coronavirus that can cause human respiratory disease. The development of a detection method for this virus that can lead to rapid and accurate diagnosis would be significant. In this study, we established a nucleic acid visualization technique that combines the reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique and a vertical flow visualization strip (RT-LAMP-VF) to detect the N gene of MERS-CoV. The RT-LAMP-VF assay was performed in a constant temperature water bath for 30 min, and the result was visible by the naked eye within 5 min. The RT-LAMP-VF assay was capable of detecting 2 × 101 copies/μl of synthesized RNA transcript and 1 × 101 copies/μl of MERS-CoV RNA. The method exhibits no cross-reactivities with multiple CoVs including SARS-related (SARSr)-CoV, HKU4, HKU1, OC43 and 229E, and thus exhibits high specificity. Compared to the real-time RT-PCR (rRT-PCR) method recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO), the RT-LAMP-VF assay is easy to handle, does not require expensive equipment and can rapidly complete detection within 35 min.
Keywords: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; RT-LAMP-VF; nucleic acid visualization; reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification; visual detection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Visual Assay of a Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Based Vertical Immunoassay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA Detection.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jul 13;13:932698. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.932698. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35903482 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid visualization assay for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) by targeting the UpE and N gene.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Mar 1;15(3):e0009227. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009227. eCollection 2021 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33647020 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and Visual Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Based on Reverse Transcription-Recombinase Polymerase Amplification with Closed Vertical Flow Visualization Strip Assay.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0296622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02966-22. Epub 2023 Jan 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36622165 Free PMC article.
-
[Coronaviruses as the cause of respiratory infections].Internist (Berl). 2019 Nov;60(11):1136-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00108-019-00671-5. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31455974 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
A Novel Real-Time Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Detection Platform: Application to Diagnosis of COVID-19.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Oct 22;9:748746. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.748746. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34746104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the nucleic acid-based diagnostic tool for coronavirus.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Nov;47(11):9033-9041. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05889-3. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33025503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Diagnostic Point-of-Care Molecular Assays for SARS-CoV-2.Clin Lab Med. 2022 Jun;42(2):223-236. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2022.03.002. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Clin Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35636823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the detection of respiratory virus infection in humans.J Med Virol. 2020 Apr;92(4):408-417. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25674. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 31944312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid diagnostic methods for SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) detection: an evidence-based report.J Med Life. 2021 Jul-Aug;14(4):431-442. doi: 10.25122/jml-2021-0168. J Med Life. 2021. PMID: 34621365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Molecular Diagnostics for COVID-19.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Nov 10;10:560616. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.560616. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33244462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhadra S., Jiang Y. S., Kumar M. R., Johnson R. F., Hensley L. E., Ellington A. D. (2015). Real-time sequence-validated loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for detection of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). PLoS One 10:e0123126. 10.1371/journal.pone.0123126 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J. F., Choi G. K., Tsang A. K., Tee K. M., Lam H. Y., Yip C. C., et al. (2015). Development and evaluation of novel real-time reverse transcription-PCR Assays with locked nucleic acid probes targeting leader sequences of human-pathogenic coronaviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 53 2722–2726. 10.1128/JCM.01224-15 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

