Effects of forkhead box protein M1 on trophoblast invasion and its role in preeclampsia development
- PMID: 29896240
- PMCID: PMC5995065
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6195
Effects of forkhead box protein M1 on trophoblast invasion and its role in preeclampsia development
Abstract
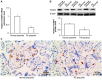
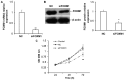
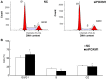
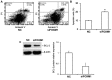
The present study aimed to investigate the expression of the forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1) in the placenta of patients with preeclampsia, and its effect on trophoblasts. A total of 28 patients with preeclampsia and 30 patients without preeclampsia (controls) who underwent cesarean section and were admitted to the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University between June 2013 and September 2016 were enrolled in the present study. The expression of FOXM1 in placental tissues was examined by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction, western blotting and immunohistochemistry. HTR8/SVneo cells were used to measure the in vitro expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The results demonstrated that FOXM1 expression was downregulated in the placental tissues of patient with preeclampsia (P<0.05). Following the silencing of FOXM1 expression, the proliferation of HTR8/SVneo cells was suppressed. The results of flow cytometry demonstrated that proportion of HTR8/SVneo cells in the G0/G1 phase and the proportion of apoptotic cells increased. The expression of the apoptosis regulator BCL-2, as well as the expression of VEGF mRNA and protein expression were also downregulated following FOXM1 silencing. FOXM1 may therefore promote the development of preeclampsia via the VEGF signaling pathway.
Keywords: forkhead box protein M1; preeclampsia; trophoblast; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
microRNA-21 regulates the proliferation of placental cells via FOXM1 in preeclampsia.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):1871-1878. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8930. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32782495 Free PMC article.
-
[Expression and significance of SATB1 and wnt/β-catenin signaling molecule in the placenta of preeclampsia].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Apr;50(4):283-90. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26080941 Chinese.
-
Reduced FOXM1 Expression Limits Trophoblast Migration and Angiogenesis and Is Associated With Preeclampsia.Reprod Sci. 2019 May;26(5):580-590. doi: 10.1177/1933719118778798. Epub 2018 May 30. Reprod Sci. 2019. PMID: 29848205
-
Wnt5a inhibited human trophoblast cell line HTR8/SVneo invasion: implications for early placentation and preeclampsia.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016 Nov;29(21):3532-8. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2016.1138102. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016. PMID: 26865089
-
lncRNA FAM99A is downregulated in preeclampsia and exerts a regulatory effect on trophoblast cell invasion, migration and apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):1451-1458. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10350. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31173227
Cited by
-
Dietary intake and serum concentrations of vitamin A and vitamin E and pre-eclampsia risk in Chinese pregnant women: A matched case-control study.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 30;10:1049055. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1049055. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37063333 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased circUBAP2 Expression Is Associated with Preeclampsia by Limiting Trophoblast Cell Proliferation and Migration.Reprod Sci. 2021 Aug;28(8):2237-2245. doi: 10.1007/s43032-020-00450-w. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Reprod Sci. 2021. PMID: 33502747 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of transcription factors that regulate placental sFLT1 expression.Mol Hum Reprod. 2025 Jul 3;31(3):gaaf031. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaaf031. Mol Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40632597 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Inflammatory Genes as Predictors of Preeclampsia: A Systematic Review.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Dec;16(Suppl 5):S4324-S4326. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1134_24. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 40061749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooks SA, Martin E, Smeester L, Grace MR, Boggess K, Fry RC. miRNAs as common regulators of the transforming growth factor (TGF)-β pathway in the preeclamptic placenta and cadmium-treated trophoblasts: Links between the environment, the epigenome and preeclampsia. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016;98:50–57. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.06.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zuckerwise L, Li J, Lu L, Men Y, Geng T, Buhimschi CS, Buhimschi IA, Bukowski R, Guller S, Paidas M, et al. H19 long noncoding RNA alters trophoblast cell migration and invasion by regulating TβR3 in placentae with fetal growth restriction. Oncotarget. 2016;7:38398–38407. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
