Automatic tube potential selection with tube current modulation in coronary CT angiography: Can it achieve consistent image quality among various individuals?
- PMID: 29896246
- PMCID: PMC5995055
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6158
Automatic tube potential selection with tube current modulation in coronary CT angiography: Can it achieve consistent image quality among various individuals?
Abstract
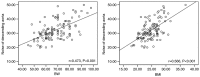
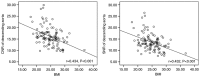
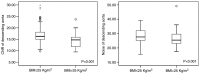
The present study included a total of 111 consecutive patients who had undergone coronary computed tomography (CT) angiography, using a first-generation dual-source CT with automatic tube potential selection and tube current modulation. Body weight (BW) and body mass index (BMI) were recorded prior to CT examinations. Image noise and attenuation of the proximal ascending aorta (AA) and descending aorta (DA) at the middle level of the left ventricle were measured. Correlations between BW, BMI and objective image quality were evaluated using linear regression. In addition, two subgroups based on BMI (BMI ≤25 and >25 kg/m2) were analyzed. Subjective image quality, image noise, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were all compared between those. The image noise of the AA increased with the BW and BMI (BW: r=0.453, P<0.001; BMI: r=0.545, P<0.001). The CNR and SNR of the AA were inversely correlated with BW and BMI, respectively. The image noise of the DA and the CNR and SNR of the DA exhibited a similar association to those with the BW or BMI. The BMI >25 kg/m2 group had a significant increase in image noise (33.1±6.9 vs. 27.8±4.0 HU, P<0.05) and a significant reduction in CNR and SNR, when compared with those in the BMI ≤25 kg/m2 group (CNR: 18.9±4.3 vs. 16.1±3.7, P<0.05; SNR: 16.0±3.8 vs. 13.6±3.2, P<0.05). Patients with a BMI of ≤25 kg/m2 had more coronary artery segments scored as excellent, compared with patients with a BMI of >25 kg/m2 (P=0.02). In conclusion, this method is not able to achieve a consistent objective image quality across the entire patient population. The impact of BW and BMI on objective image quality was not completely eliminated. BMI-based adjustment of the tube potential may achieve a more consistent image quality compared to automatic tube potential selection, particularly in patients with a larger body habitus.
Keywords: body mass index; contrast-to-noise ratio; coronary computed tomography angiography; image consistency; image noise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CT Pulmonary Angiography Using Automatic Tube Current Modulation Combination with Different Noise Index with Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm in Different Body Mass Index: Image Quality and Radiation Dose.Acad Radiol. 2016 Dec;23(12):1513-1520. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.07.018. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Acad Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27717760
-
Volumetric Single-Beat Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography: Relationship of Image Quality, Heart Rate, and Body Mass Index. Initial Patient Experience With a New Computed Tomography Scanner.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016 Sep-Oct;40(5):763-72. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000428. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016. PMID: 27331931
-
Automated tube voltage selection for radiation dose and contrast medium reduction at coronary CT angiography using 3(rd) generation dual-source CT.Eur Radiol. 2016 Oct;26(10):3608-16. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-4191-4. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26847044
-
Image quality and radiation reduction of 320-row area detector CT coronary angiography with optimal tube voltage selection and an automatic exposure control system: comparison with body mass index-adapted protocol.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Jun;31 Suppl 1:23-30. doi: 10.1007/s10554-015-0594-1. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25604967
-
Radiation and contrast agent doses reductions by using 80-kV tube voltage in coronary computed tomographic angiography: a comparative study.Eur J Radiol. 2014 Feb;83(2):309-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.06.032. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Eur J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24315475 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Ladder-Like Low Iodine Delivery Rate Injection Protocols Based on BMI at 70 KV by Automated Tube Voltage Selection in Coronary CTA.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jul 16;2022:7804015. doi: 10.1155/2022/7804015. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35924071 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Explore the Value of Dual Source Computer Tomography Automatic Tube Current Regulation in Reducing the Radiation Dose of CTA in Lower Extremity Vessels.Front Surg. 2022 May 3;9:896370. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.896370. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35592130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delewi R, Hoebers LP, Råmunddal T, Henriques JP, Angerås O, Stewart J, Robertsson L, Wahlin M, Petursson P, Piek JJ, et al. Clinical and procedural characteristics associated with higher radiation exposure during percutaneous coronary interventions and coronary angiography. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:501–506. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.113.000220. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Halliburton SS, Abbara S, Chen MY, Gentry R, Mahesh M, Raff GL, Shaw LJ, Hausleiter J. Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography: SCCT guidelines on radiation dose and dose-optimization strategies in cardiovascular CT. J Cardiovasc Computed Tomography. 2011;5:198–224. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2011.06.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
