Base-catalyzed synthesis of aryl amides from aryl azides and aldehydes
- PMID: 29896355
- PMCID: PMC5952891
- DOI: 10.1039/c5sc03510d
Base-catalyzed synthesis of aryl amides from aryl azides and aldehydes
Abstract
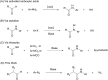
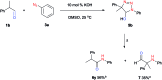
Aryl amides have been used as important compounds in pharmaceuticals, materials and in molecular catalysis. The methods reported to prepare aryl amides generally require very specific reagents, and the most popular carboxyl-amine coupling reactions demand stoichiometric activators. Herein, we report that aryl azides react with aldehydes under base-catalyzed conditions to yield aryl amides efficiently. Mechanistic investigations support the formation of triazoline intermediates via azide-enolate cycloaddition, which subsequently undergo rearrangement to give amides by either thermal decomposition (20-140 °C) or aqueous acid work-up at room temperature. The strategy does not require nucleophilic anilines and is especially efficient for highly electron-deficient aryl amides, including perfluoroaryl amides, which are otherwise challenging to synthesize.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Electrophilic Azides for Materials Synthesis and Chemical Biology.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Apr 21;53(4):937-948. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00046. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 32207916 Review.
-
N,N-diethylurea-catalyzed amidation between electron-deficient aryl azides and phenylacetaldehydes.Org Lett. 2015 Feb 6;17(3):636-9. doi: 10.1021/ol503655a. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Org Lett. 2015. PMID: 25616121 Free PMC article.
-
Azide-Enolate Cycloaddition-Rearrangement Enables Direct α-Amination of Amides and Enelactam Synthesis from Esters.Chemistry. 2023 Jun 2;29(31):e202300261. doi: 10.1002/chem.202300261. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 36849870
-
Reaction of azides and enolisable aldehydes under the catalysis of organic bases and Cinchona based quaternary ammonium salts.Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Jun 21;15(24):5227-5235. doi: 10.1039/c7ob00799j. Org Biomol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28598472
-
From α-arylation of olefins to acylation with aldehydes: a journey in regiocontrol of the Heck reaction.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Aug 16;44(8):614-26. doi: 10.1021/ar200053d. Epub 2011 May 25. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21612205 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods for direct C(sp2)-H bonds azidation.RSC Adv. 2019 Aug 13;9(43):25199-25215. doi: 10.1039/c9ra04534a. eCollection 2019 Aug 8. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35528700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Carbohydrate-Grafted Glycopolymers Using a Catalyst-Free, Perfluoroarylazide-Mediated Fast Staudinger Reaction.Molecules. 2019 Jan 3;24(1):157. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010157. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30609799 Free PMC article.
-
Base-Promoted SNAr Reactions of Fluoro- and Chloroarenes as a Route to N-Aryl Indoles and Carbazoles.Molecules. 2019 Mar 22;24(6):1145. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061145. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30909464 Free PMC article.
-
A Selective Single Step Amidation of Polyfluoroarenes.J Fluor Chem. 2021 Aug;248:109821. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2021.109821. Epub 2021 May 30. J Fluor Chem. 2021. PMID: 35027775 Free PMC article.
-
One-Pot Tandem Assembly of Amides, Amines, and Ketones: Synthesis of C4-Quaternary 3,4- and 1,4-Dihydroquinazolines.J Org Chem. 2020 Sep 4;85(17):11211-11225. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c01308. Epub 2020 Aug 21. J Org Chem. 2020. PMID: 32786625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghose A. K., Viswanadhan V. N., Wendoloski J. J. J. Comb. Chem. 1999;1:55–68. - PubMed
-
- Liu D., Choi S., Chen B., Doerksen R. J., Clements D. J., Winkler J. D., Klein M. L., DeGrado W. F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004;43:1158–1162. - PubMed
-
- Ugur G., Chang J., Xiang S., Lin L., Lu J. Adv. Mater. 2012;24:2685–2690. - PubMed
-
- Shen X., Viney C., Johnson E. R., Wang C., Lu J. Q. Nat. Chem. 2013;5:1035–1041. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

