Evaluation of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment in Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury in Rats Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
- PMID: 29896427
- PMCID: PMC5988594
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2017.0726
Evaluation of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment in Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury in Rats Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Abstract
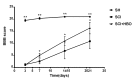
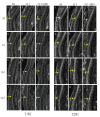
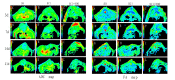
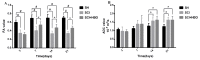
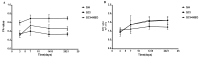
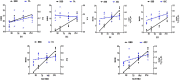
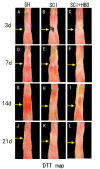
This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect of hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) on acute spinal cord injury (SCI) by measuring the in vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) and observing diffusion tensor tractography (DTT) of fiber bundle morphology. The rats were randomly divided into sham-operated (SH), SCI, and SCI and hyperbaric oxygen treatment (SCI + HBO) groups (n = 6 in each group). The Basso-Bettie-Bresnahan (BBB) score was used to evaluate motor function recovery, and DTI was performed on days 3, 7, 14, and 21 after surgery. BBB scores and FA values decreased significantly after SCI, while the two values significantly improved in the SCI + HBO group compared with the SCI group on days 7, 14, and 21. ADC increased significantly on days 14 and 21 postoperatively in the SCI group compared with the SH group but did not significantly differ between the SCI and SCI + HBO groups at any time point. BBB scores had the same variation trend with ADC values and FA values in all three groups. In the SH group, DTT showed a well-organized spinal cord, but the spinal cord showed interruptions at sites of injury after SCI. In conclusion, HBO promotes the recovery of neuronal function after SCI. Parameters of DTI, especially FA, can quantitatively evaluate the efficacy of HBO treatment in SCI, while DTT enables the visualization of the fiber tracking of spinal cord tracts.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; hyperbaric oxygen; spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Additional Information Competing financial interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for spinal cord injury in rats with different treatment course using diffusion tensor imaging.Spinal Cord. 2019 May;57(5):404-411. doi: 10.1038/s41393-018-0238-0. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Spinal Cord. 2019. PMID: 30643168
-
Effect of VEGF and CX43 on the promotion of neurological recovery by hyperbaric oxygen treatment in spinal cord-injured rats.Spine J. 2014 Jan;14(1):119-27. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.06.084. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24183749
-
Hyperbaric oxygen intervention on expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in spinal cord injury models in rats.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013 Oct;126(20):3897-903. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 24157153
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging in the diagnosis, prognosis, and assessment of recovery and treatment of spinal cord injury: a systematic review.Neurosurg Focus. 2019 Mar 1;46(3):E7. doi: 10.3171/2019.1.FOCUS18591. Neurosurg Focus. 2019. PMID: 30835681
-
Role of diffusion tensor imaging and tractography in spinal cord injury.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022 Aug 31;33:101997. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2022.101997. eCollection 2022 Oct. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022. PMID: 36118562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of b Value on Imaging Quality for Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Spinal Cord at Ultrahigh Field Strength.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jan 6;2021:4836804. doi: 10.1155/2021/4836804. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33506018 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for spinal cord injury in rats with different treatment course using diffusion tensor imaging.Spinal Cord. 2019 May;57(5):404-411. doi: 10.1038/s41393-018-0238-0. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Spinal Cord. 2019. PMID: 30643168
-
The mechanism by which hyperbaric oxygen treatment alleviates spinal cord injury: genome-wide transcriptome analysis.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Dec;17(12):2737-2742. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.339498. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35662222 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for spinal cord injury: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 4;99(49):e23536. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023536. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33285769 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the neuroprotective effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy.Med Gas Res. 2021 Apr-Jun;11(2):72-82. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.311498. Med Gas Res. 2021. PMID: 33818447 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ducreux D, Fillard P, Facon D, Ozanne A, Lepeintre JF, Renoux J, et al. (2007). Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord lesions: current and future indications. Neuroimaging Clin N Am, 17: 137-47 - PubMed
-
- Nakamura M, Fujiyoshi K, Tsuji O, Konomi T, Hosogane N, Watanabe K, et al. (2012). Clinical significance of diffusion tensor tractography as a predictor of functional recovery after laminoplasty in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine, 17: 147-52 - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M, Toyama Y, Ishikawa M, Chiba K, Suzuki N, Fujimura Y (2000). Increased signal intensity of the spinal cord on magnetic resonance images in cervical compressive myelopathy. Does it predict the outcome of conservative treatment? Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 25: 677-82 - PubMed
-
- DeBoy CA, Zhang J, Dike S, Shats I, Jones M, Reich DS, et al. (2007). High resolution diffusion tensor imaging of axonal damage in focal inflammatory and demyelinating lesions in rat spinal cord. Brain, 130: 2199-210 - PubMed
-
- Ellingson BM, Schmit BD, Kurpad SN (2010). Lesion growth and degeneration patterns measured using diffusion tensor 9.4-T magnetic resonance imaging in rat spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine, 13: 181-92 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
